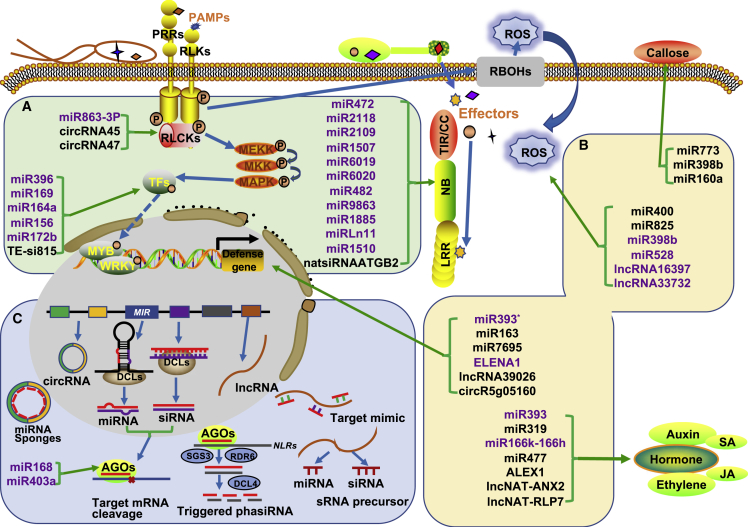
Figure 1.
ncRNAs involved in plant immunity and their underlying regulation.
(A) ncRNAs that regulate immune signaling components. Some ncRNAs target immune receptor PPRs and NLRs such as FLS2 and RPS5, which mediate pathogen perception. Other ncRNAs regulate RLCKs and TFs such as SpRLK and WRKY45, which are involved in immune signal transduction.
(B) ncRNAs that directly or indirectly modulate various biological processes of PTI or ETI response, including ROS accumulation, callose deposition, defense-related gene expression, and plant hormone regulation, to regulate plant immunity.
(C) Coordinated function among ncRNAs in immunity. miRNAs targeting NLR genes can trigger the production of phasiRNAs. lncRNAs mainly serve as target mimics and miRNA/siRNA precursors. circRNAs may act as decoys for miRNAs to upregulate the expression of mRNAs targeted by miRNAs. Abbreviations: PAMPs, pathogen-associated molecular patterns; PRRs, pattern recognition receptors; RLKs, receptor-like kinases; RLCKs, receptor-like cytosolic kinases; TFs, transcription factors; P, phosphorylation; ROS, reactive oxygen species; DCL, DICER-LIKE; AGO, ARGONAUTE; SGS3, SUPPRESSOR OF GENE SILENCING 3; RDR6, RNA-DEPENDENT RNA POLYMERASE 6; phasiRNA, phased secondary small interfering RNA. ncRNAs marked in purple directly regulate immune signaling components and downstream responses, whereas those marked in black have indirect or unknown mechanisms of regulation. Red lines represent miRNAs and siRNAs.