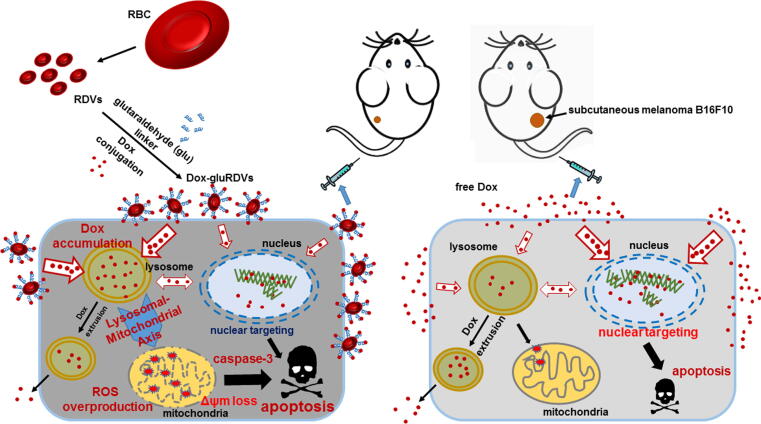
Fig. 6.
Schematic illustration of the superior anticancer activity of Dox-gluRDVs. A systemic bDDS (RDVs) of doxorubicin is developed for improved cancer therapy. The as-synthesized Dox-gluRDVs demonstrated superior in vivo anticancer activity in subcutaneous melanoma B16F10-bearing mice through intravenous administration. A novel lysosomal-mitochondrial axis-dependent cell death mechanism is revealed: Dox-gluRDVs can efficiently deliver Dox into lysosomes, resulting in the accumulation of adequate quantities of Dox to consequently fuel the mitochondrial ROS overproduction, and subsequently resulting in mitochondrial membrane potential loss and apoptotic activation, which is responsible for superior anticancer activity of Dox-gluRDVs in vitro and in vivo.