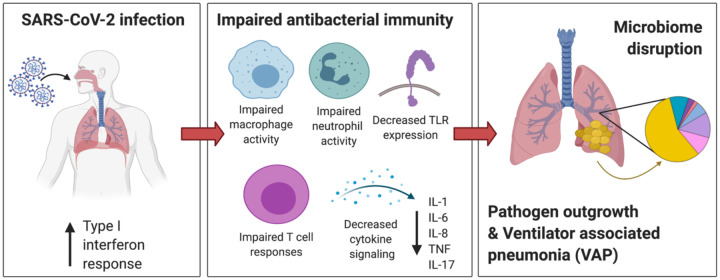
Figure 7: Mechanistic hypothesis of secondary bacterial pneumonia susceptibility in patients with COVID-19.
Individual immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection drive a restructuring of the microbial community and increase susceptibility to VAP. Those predisposed to VAP have increased type I interferon responses and dysregulated antibacterial immune signaling characterized by impaired macrophage, neutrophil and T cell activity, decreased TLR signaling and impaired activation of key cytokines important for pathogen defense including IL-1, IL-6, IL-8, TNF, and IL-17. This state of suppressed immunity disrupts the lower respiratory tract microbiome, predisposing to outgrowth of bacterial pathogens and VAP.