Figure 4.
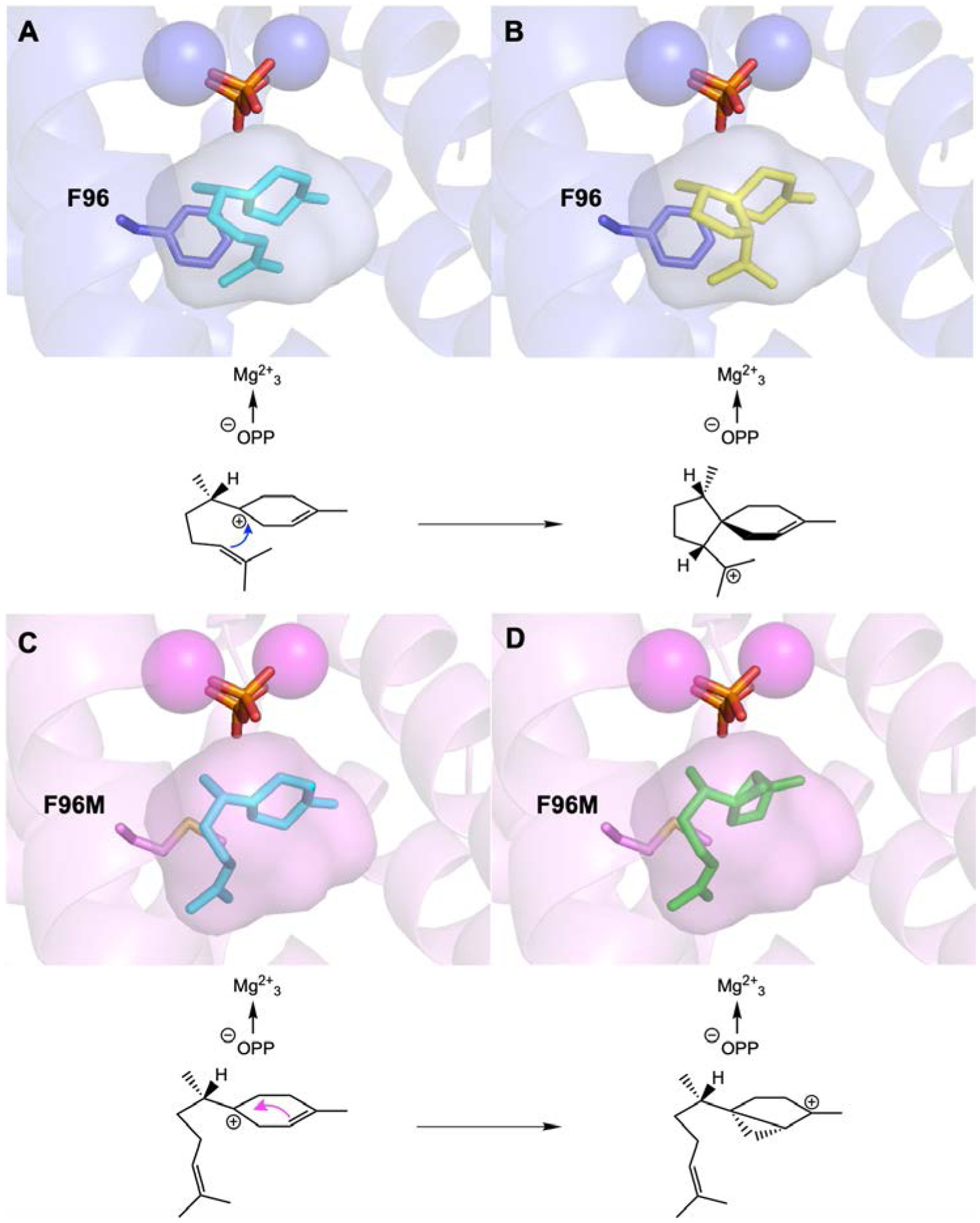
Models of wild-type EIZS and F96M EIZS complexed with carbocation intermediates. Wild-type EIZS (PDB 3KB9) with the (7S)-homobisabolyl cation (cyan) (A) and the (1S,4R,5R)-acorenyl cation (yellow) (B) docked in the active site. This reaction sequence leads to epi-isozizaene formation. F96M EIZS (PDB 7KJG) with the (7S)-homobisabolyl cation (cyan) (C) and the (1S,5S,6S)-sesquisabinyl cation (green) (D) docked in the active site. This reaction sequence leads to sesquisabinene A formation. The active site contour of F96M is slightly larger and is unable to hold the isoprenoid tail of the homobisabolyl cation sufficiently close for acorenyl cation formation.
