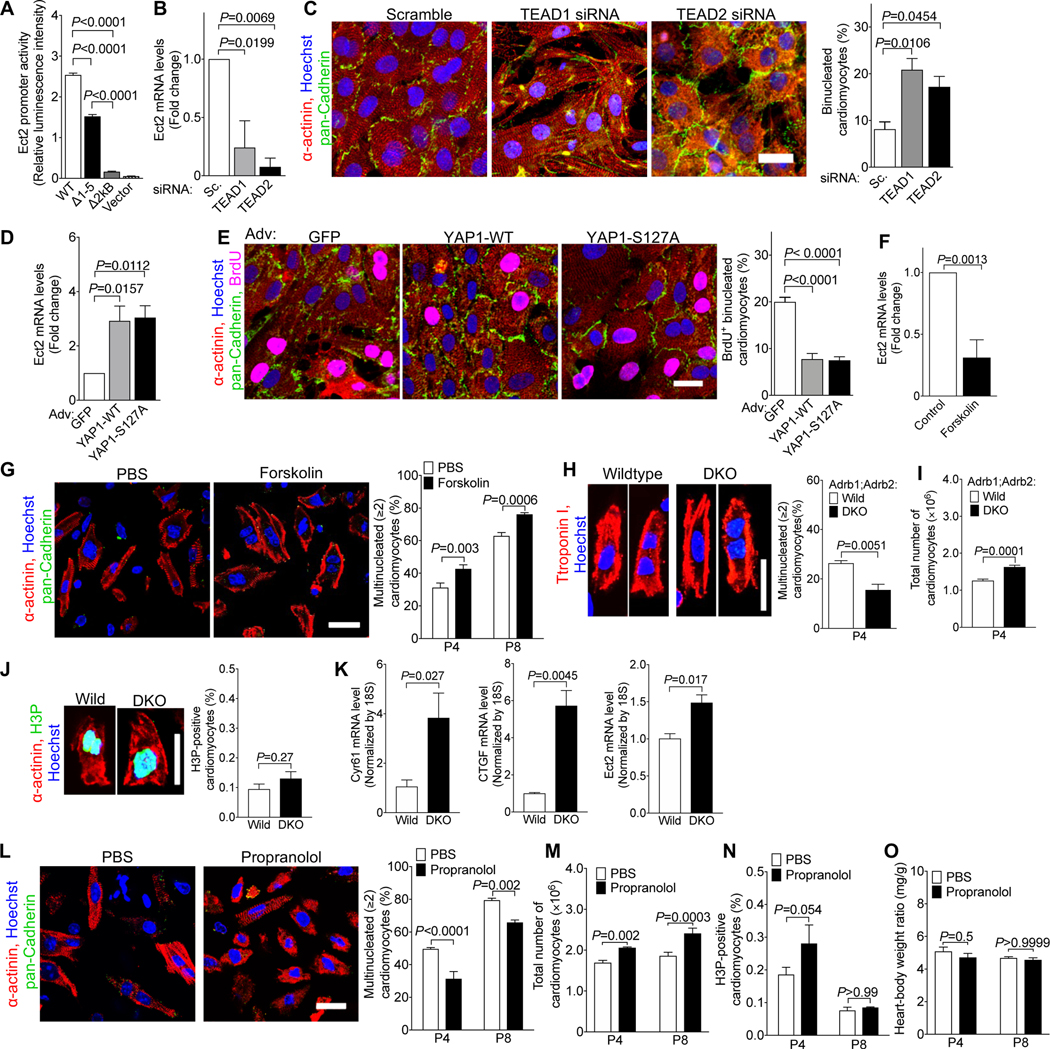
Figure 3. β-adrenergic receptor signaling regulates cardiomyocyte abscission and endowment in mice.
(A) Removal of the five TEAD1/2-binding sites (Fig. S7) reduced the activity of the Ect2 promoter in luciferase assays in HEK293 cells. WT: wild type Ect2 promoter; Δ1–5: All five putative TEAD-binding sites were removed; Δ2kB: the continuous 2kB DNA sequence containing all five TEAD-binding sites was removed; Vector: Empty vector that did not contain Ect2 promoter (n = 4 cultures). (B, C) Knockdown of TEAD1 and TEAD2 by siRNA reduced Ect2 mRNA (B), and increased the proportion of binucleated NRVMs (P2, C, n = 3 cardiomyocyte isolations). (D-E) Adenoviral overexpression of wild type YAP1 (YAP1-WT) and a mutated version containing a S127A mutation (YAP1-S127A) in NRVMs (P2) increased the level of Ect2 mRNA (D) and reduced the percentage of binucleated cardiomyocytes (E, n = 4 cardiomyocyte isolations). (F) Forskolin reduced the mRNA level of Ect2 in cultured NRVMs (n = 5 cardiomyocyte isolations). (G) Forskolin administration (1 μg/g, 1 i.p. injection per day) increased the proportion of binucleated cardiomyocytes in vivo (n = 6 hearts/group). (H-K) Inactivation of β1- and β2-adrenergic receptor genes (DKO) decreased formation of multinucleated cardiomyocytes in vivo (H, n = 4 hearts/group), increased the total number of cardiomyocytes (I, n = 7 hearts for wild, n = 5 hearts for DKO), did not change M-phase (J, n = 4 hearts/group), and increased the expression of the YAP target genes Cyr61 and CTGF (K, n = 3 hearts/group). (L-O) Propranolol administration (10 μg/g, 2 i.p. injections per day) reduced the proportion of multinucleated cardiomyocytes (L, n = 6 hearts/group), and increased the number of cardiomyocytes (M, n = 6 heart/group for P4, n = 4 hearts/group for P8), but did not alter M-phase activity (N, n = 4 hearts/group) or heart-body-weight ratio (O, P4: n = 7 hearts for PBS, n = 6 hearts for Prop; P8: n = 4 hearts/group). Scale bar: 20 μm (C, E, G, H, J, L). Statistical significance was tested with one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons (A-E), Student’s t- test (F, H-K), and two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test (G, L-O).