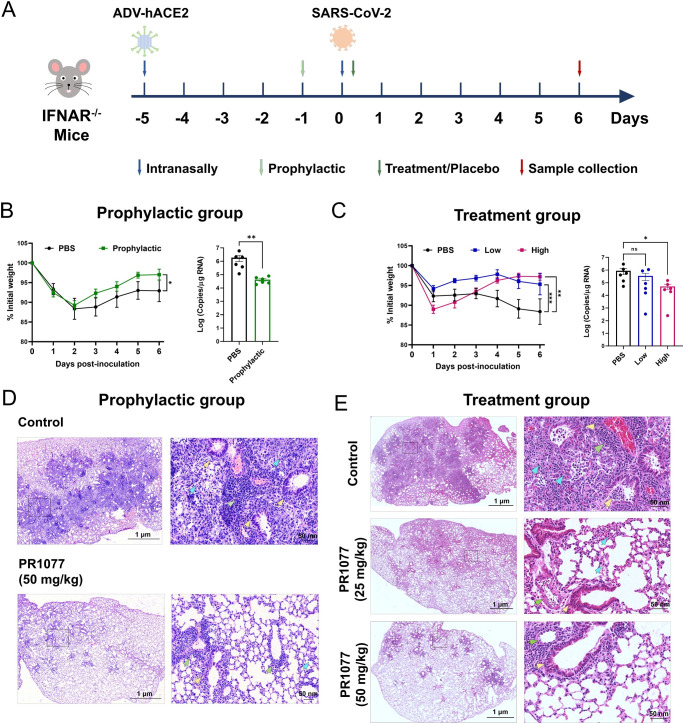
Fig 5. Therapeutic efficacy of PR1077 in SARS-CoV-2–infected AdV-hACE2-transduced mice.
(A) Experimental design for PR1077 neutralization activity testing in AdV-hACE2-transduced IFNAR−/− mice. (B, C) Body weight changes and viral copies in the lung of infected mice were monitored. (B) For prophylactic efficacy testing, mice were intraperitoneally injected with 50 mg/kg of PR1077 or 200 μl PBS (n = 6 per group) at 24 hours before SARS-CoV-2 infection. All the data of this figure can be found in the S9 Data file. (C) For therapeutic efficacy testing, the animals were treated with PBS, 50 mg/kg, or 25 mg/kg of PR1077 at 2 h p.i. (n = 6 per group). Weight changes were monitored daily, and viral copies in the lungs were measured at 6 d p.i. by qRT-PCR. All the data of this figure can be found in the S10 Data file. (D, E) Histopathological analyses of PR1077 treated or untreated mice infected with SARS-CoV-2. Representative images of lung sections stained by HE in the PR1077 prophylactic (D) and treatment (E) groups at 6 d p.i. a. Data are mean ± SEM. Blue, yellow, and green arrows indicate the pathological changes in the alveoli, bronchi/bronchioles, and blood vessels, respectively. The images on the right (bars = 1 μm) are enlarged regions in the dashed boxes of the left images (bars = 50 nm). d.p.i., days post-infection; hACE2, human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; HE, hematoxylin–eosin; h.p.i., hours post-infection; qRT-PCR, quantitative real-time PCR; SARS-CoV-2, Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2.