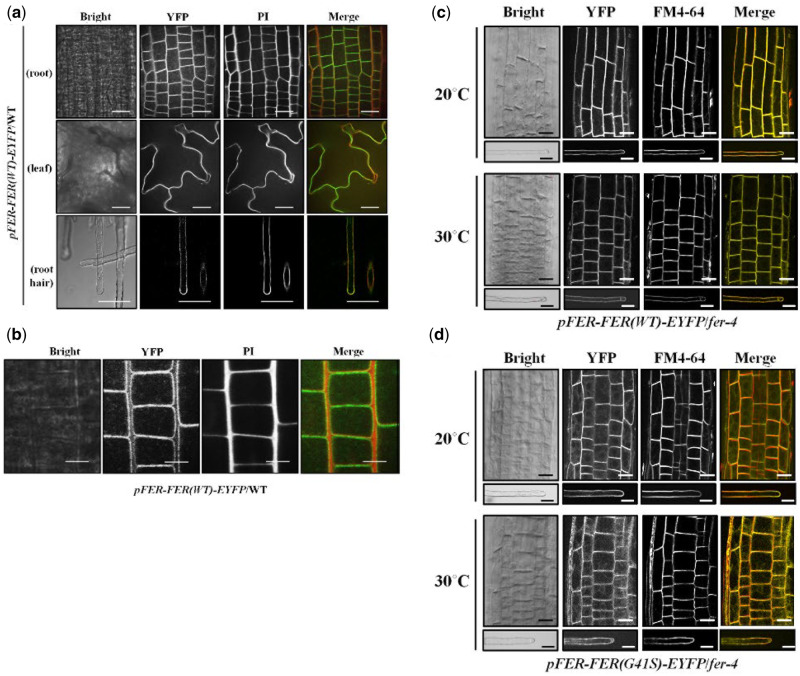
Figure 7.
Subcellular localization of FER(WT)-EYFP and FER(G41S)-EYFP fluorescent fusion proteins in stably transformed Arabidopsis. (A) Subcellular localization of FER(WT)-EYFP protein in various tissues. Fluorescent confocal images displaying the subcellular distribution of FER(WT)-EYFP protein were detected from growing root, leaf and root hair cells of 7-d-old seedlings in pFER-FER(WT)-EYFP/WT transgenic plants. Cell walls were counter-stained by incubating for 5 min in a PI solution (10 µg/ml). Images were collected by spinning-disk fluorescence confocal microscopy using a Zeiss 40× Plan-Apochromat (1.3 NA) lens with appropriate EYFP and PI fluorescence filter sets. Scale bars = 20 µm. (B) Magnified images of FER(WT)-EYFP fluorescence. FER(WT)-EYFP in WT of growing root cells of 7-d-old Arabidopsis seedlings was detected by spinning-disc confocal microscopy using a Zeiss 100× Plan-Apochromat (1.46 NA) oil immersion objective with appropriate EYFP and PI filter sets. Scale bars = 10 µm. (C and D) Subcellular localization of FER(WT)-EYFP (C) and FER(G41S)-EYFP (D) fluorescent fusions in root and root hair cells at normal (20°C) and elevated (30°C) temperatures. Cells from fer-4 plants stably transformed and homozygous for FER(WT)-EYFP or FER(G41S)-EYFP were counterstained with FM4-64 (5 µM) for 5 min to visualize cell membranes. Images were collected by spinning-disk fluorescence confocal microscopy using a Zeiss 40× Plan-Apochromat (1.3 NA) lens with appropriate EYFP and FM4-64 fluorescence filter sets. Scale bars = 20 µm; root, 10 µm; root hair.