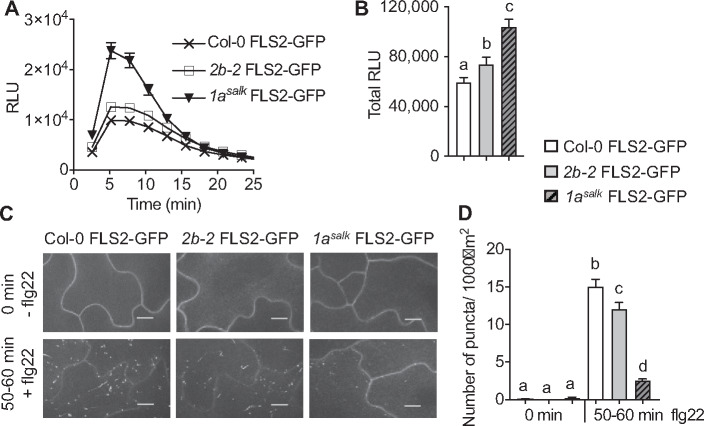
Figure 5.
DRP1A has a prominent role in flg22-induced endocytosis of FLS2-GFP. A, Time-course of 1 µM flg22-induced ROS production in cotyledons of 7-d-old Col-0 FLS2-GFP, drp1asalk FLS2-GFP and drp2b-2 FLS2-GFP mutant seedlings. n = 24 biological samples/genotype, with each n consisting of two halves of a cotyledon. B, Total 1 µM flg22-induced ROS production from time-course shown in A. For C and D, Col-0 FLS2-GFP, drp2b-2 FLS2-GFP, and drp1asalk FLS2-GFP homozygous seedlings were treated with 1 µM flg22 for 0 and 50–60 min to examine ligand-induced endocytosis of FLS2-GFP on the adaxial surface of the cotyledon epidermis using SDCM. C, Representative maximum-intensity projection images of FLS2-GFP fluorescence. Scale bars = 10 µm. D, Quantification of FLS2-GFP puncta at indicated times post-elicitation with n 18 images/genotype/treatment with at least six images each taken from three different seedlings per genotype and treatment. Values are means ± se with different letters denoting statistically significant difference and with same letters indicating no statistically significant differences based on ordinary one-way ANOVA (P < 0.05). All experiments were performed at least five times, with similar results using biologically distinct samples for each biological replicate. Col-0 FLS2-GFP, WT FLS2-GFP; 2b-2 FLS2-GFP, drp2b-2 FLS2-GFP; 1asalk FLS2-GFP, drp1a069077 FLS2-GFP; min, minutes; and RLU, relative light units.