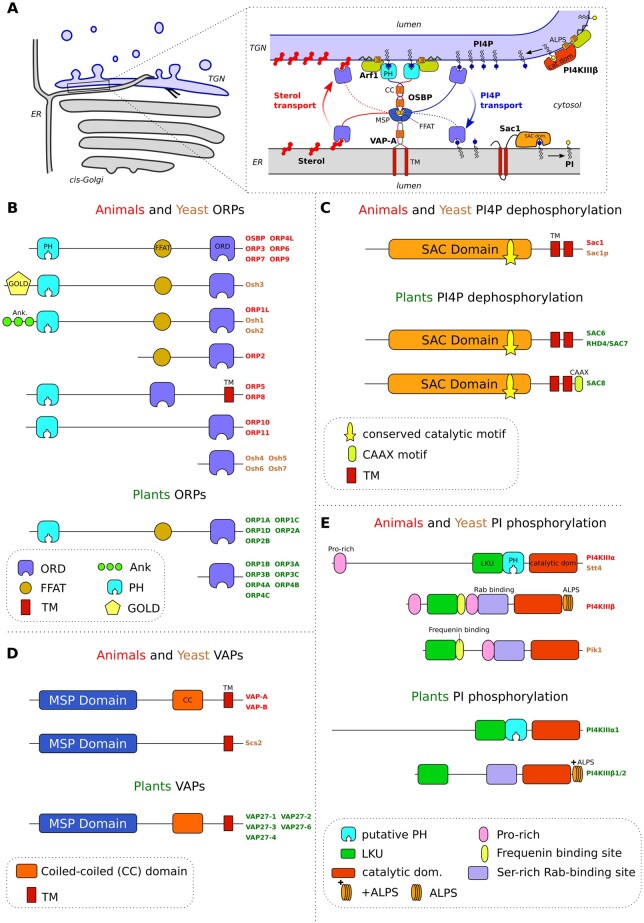
Figure 2.
ORPs, Sac1, VAPs, and PI4KIIIs in animals and yeast and their structural homologs in plants. (A) Model for OSBP-mediated cholesterol/PI4P transfer at ER/TGN contact sites in humans with some functional domains found in ORP, SAC1, VAP, and PI4K indicated. The schematic of lipid transfer is inspired by Antonny et al. (2018). (B) Animal (Homo sapiens) and yeast (S. cerevisiae) ORPs and structural homologs in plants. (C) Animal (H. sapiens) and yeast (S. cerevisiae) Sac1 proteins and structural homologs in plants. (D) Animal (H. sapiens) and yeast (S. cerevisiae) VAPs and structural homologs in plants. (E) Animal (H. sapiens) and yeast (S. cerevisiae) PI4KIIIs and structural homologs in plants. Abbreviations: OR dom., oxysterol-related domain (function in lipid transfer); FFAT, two phenylalanine in an acidic tract domain (interacts with VAP); TM, transmembrane domain; PH, pleckstrin homology domain (interaction with lipids, and with ARF1 in some cases); CAAX, putative prenylation site (lipid anchoring); MSP, major sperm protein domain (interaction with FFAT motif); ALPS, amphipathic lipid packing sensors domain (curvature sensor); +ALPS, amphipathic lipid packing sensors with adjacent cationic residues. The following domains are shown for comparison purposes between different family members but their functions are not discussed in this review: Pro-rich, proline-rich domain; Ser rich, serine-rich domain. Ank, Ankyrin domain; GOLD, Golgi-localization domain; LKU, lipid kinase unique domain.