Figure 4.
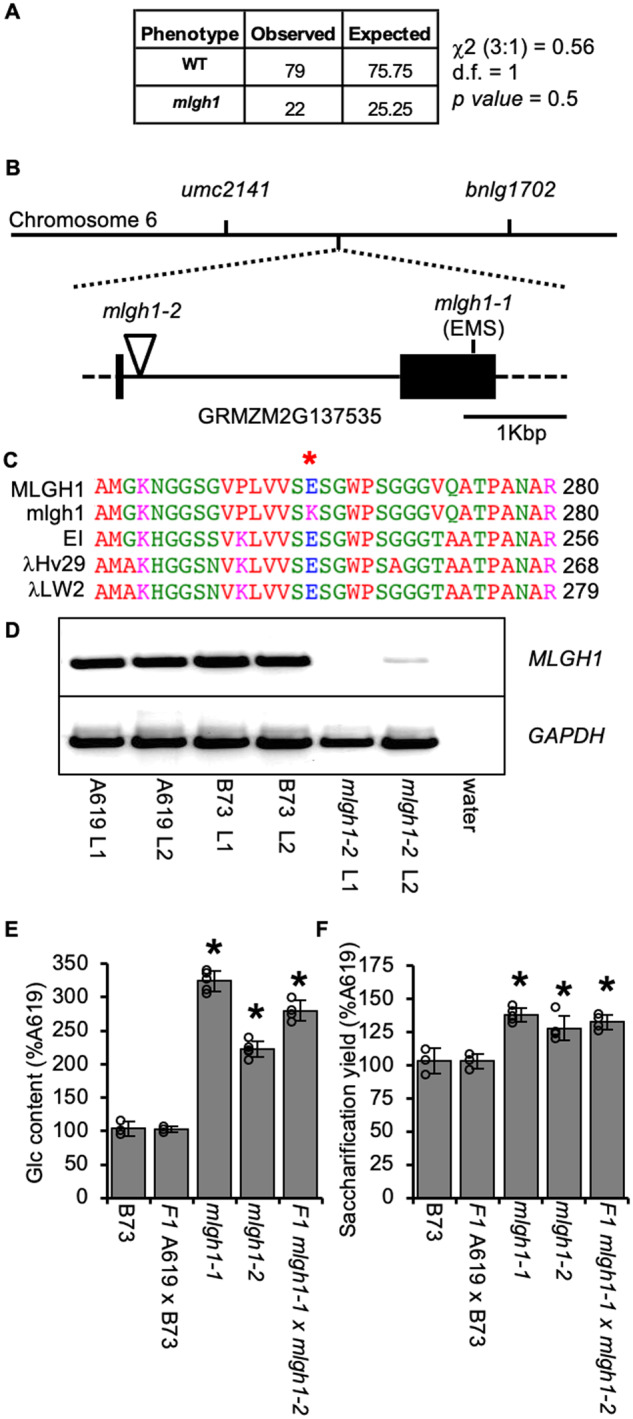
Two allelic mutants affected in the maize MLGH1 grass-specific gene encoding a putative licheninase. A, Chi-square (c2) test for a recessive segregation (3:1) of mlgh1-1 in a F2 cross to B73. d.f. = degree of freedom. P values > 0.05 means hypothesis must be accepted. B, Schematic representation of mlgh1-1 mapping on chromosome 6 between the umc2141 and bnlg1702 markers, and structure of the MLGH1 gene. Black boxes = exons; lines = introns; dashed lines = untranslated regions. Position of the mlgh1-1 and mlgh1-2 mutations is indicated. C, Detail of the protein alignment of maize MLGH1, mlgh1-1, and three highly similar licheninases from barley (EI and λHv29) and wheat (λLW2). Red asterisk indicates the mutated amino acid residue in mlgh1-1, an E262K substitution. Numbers to the right indicate the position of the last amino acid residue shown (R) related to the starting methionine. D, Agarose electrophoresis gel showing transcript level of MLGH1. RT-PCR with MLGH1-specific primers using cDNA synthetized from RNA extracted from the first (L1) and second (L2) leaf of the indicated genotypes. A negative control was included using water as template. Amplification with glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH)-specific primers was used as housekeeping control. E, Quantification of the hemicellulosic glucose (Glc) released after acid hydrolysis of dAIR material from the indicated genotypes. F, Glucose released by enzymatic digestion of dAIR from the indicated genotypes. Bars in E and F show the percentage of the A619 value. Values represent mean ± sd. Black asterisks indicate statistical differences to B73 according to Student’s t test (P < 0.05).
