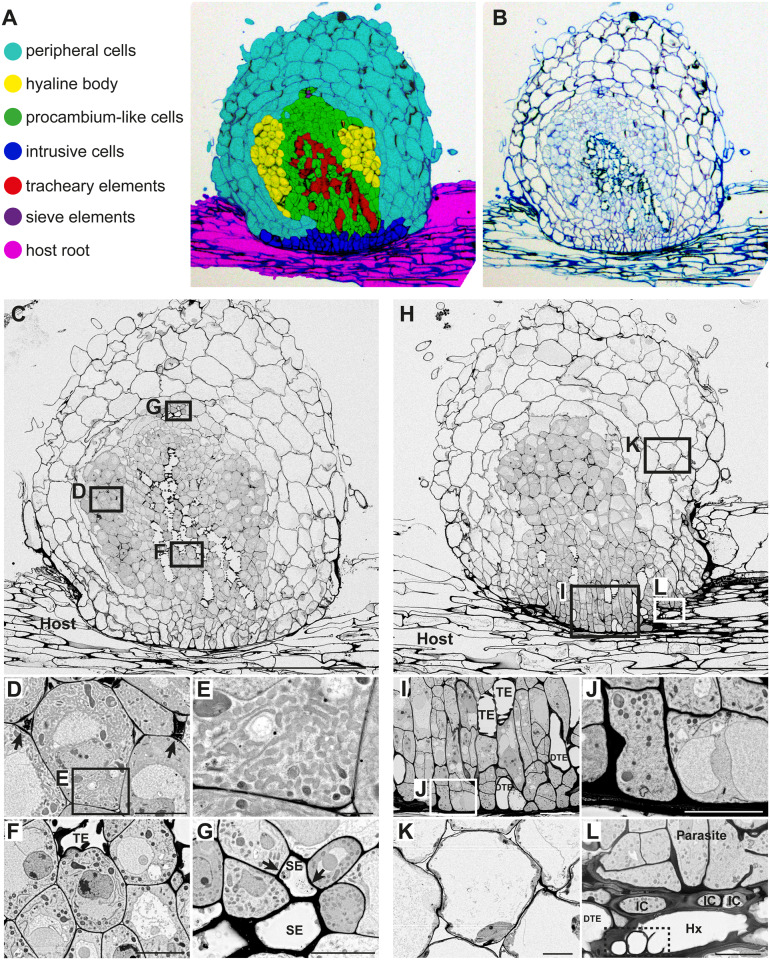
Figure 2.
Tissue distribution and morphological characteristics of haustorial cells in S. hermonthica. A, Distribution of cell types in a S. hermonthica haustorium 2 weeks after infection of a rice root. B, Original toluidine blue-stained section used in A. C, A FE-SEM image in the center of a haustorium with a focus on the xylem bridge. D, A magnified image of hyaline cells from C, showing the accumulation of electron dense extracellular materials (arrows) between hyaline cells. E, Magnification of square box in D showing smooth-ER like structures in the cytosol of a hyaline cell. F, A magnified image from C showing procambium-like cells that surround a TE. G, A magnified image of SEs from C. Phloem plastids (arrows) were observed. H, A FE-SEM image of a haustorium section with a focus on intrusive cells. I, A magnified image of intrusive cells from H. DTE: differentiating TE. J, Magnification of square box in I showing cell wall thickening at the interface between parasite and host. K, A magnified image of haustorial cortical cells from H. L, A magnified image from H showing oscula structures (dashed box) inside a host vessel element (Hx), which is surrounded by three intrusive cells (ICs) and a DTE. Scale bars, A–C, H = 200 µm; D, F, G, and J–L = 10 µm; E = 2 µm; and I = 20 µm.