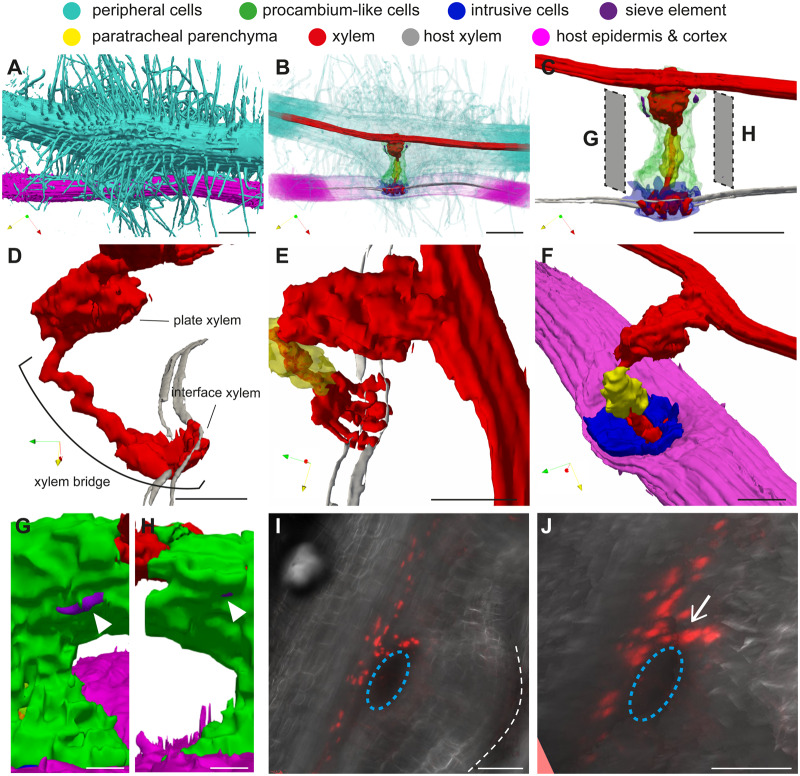
Figure 6.
3-D images of a P. japonicum haustorium. A, Surface view showing attachment of many haustorial hairs on a host root. B, Semi-transparent view of a haustorium and the host root. C, Internal haustorial cells and host root vasculature. D and E, Close-up view of a xylem bridge interacting with the host’s xylem visualized from side (D) and top (E). F, Close-up view showing that intrusive cells cover the entire interaction surface with the host. G and H, Localization of SEs (white arrowheads) in procambium-like cells. Visualization angles of G and H are indicated in C. I, Stacked confocal microscopy image for the expression of SE marker pAtPEAR1::tdTomato-nls (red signals) at 14 d after infection. White dashed line indicates the interface between haustorium and host. Blue dashed circles indicate the position of plate xylem. J, Visualization of I from a slightly different angle. Note that the nucleus-derived red signals form a continuous strand (white arrow) from those in the main vascular, indicating that haustorial SE is connected to root SE. X-, Y-, and Z-axes are indicated by red, yellow, and green arrows, respectively, in each 3-D image. Scale bars, A–C = 100 µm; D–F, I, and J = 50 µm; G and H = 20 µm. Note that the scale bars in 3-D figures indicate the length on the horizontal XY plane.