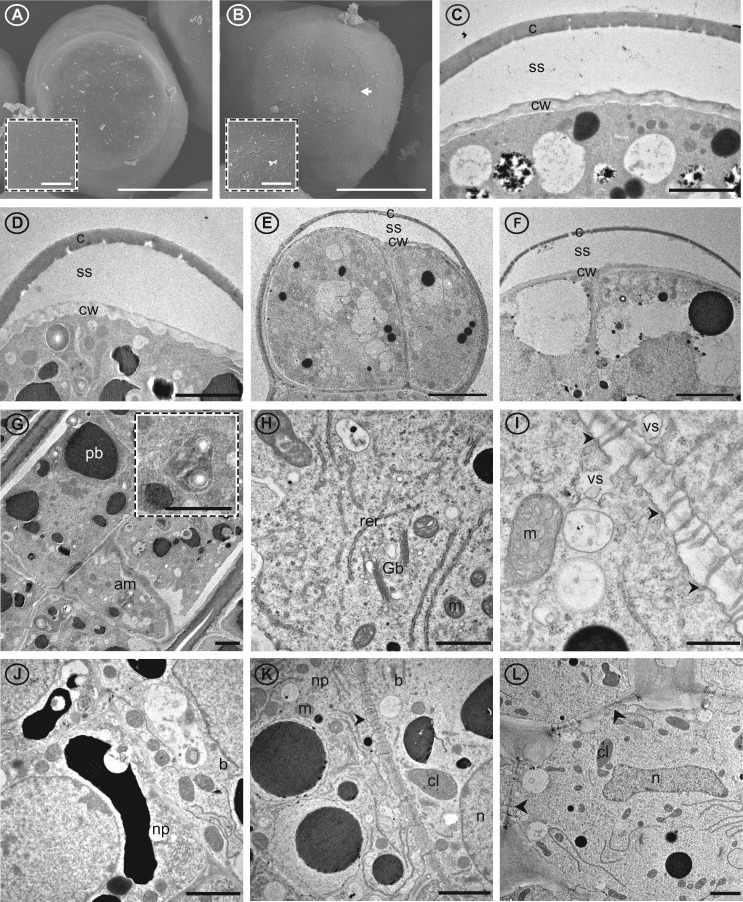
Figure 5.
Cuticle, cell wall, and cellular details of G. hirsutum nectary papillae and supporting nectariferous parenchyma tissue. Images from scanning (A and B) and transmission (C–L) electron microsopy. A, Terminal end of papillae of circumbracteal nectary at pre-secretory stage, note lack of microchannels (cracks) in cuticle surface; B, Circumbracteal secretory nectary, arrow head identifies the microchannels in the cuticle surface; C–F, Head cells from secretory papillae showing separated cuticle of (C) circumbracteal, (D) bracteal, (E) floral, and (F) foliar nectaries; G, Stalk cells from bracteal nectary with amyloplast insert; H, Organelles of stalk cell exemplified by foliar nectary; I, Plasmodesmata (arrowheads) in cell wall of internal stalk cell; J, Basal cell from circumbracteal nectary; K, Junction between basal cell and nectariferous parenchyma of bracteal nectary; L, Nectariferous parenchyma from foliar nectary. Arrowheads identify plasmodesmata. Abbreviations: am = amyloplasts; c = cuticle; cl = chloroplast; cw = cell wall; b = basal cell; er = endoplasmic reticulum; Gb = Golgi body; m = mitochondria; n = nucleus; np = nectariferous parenchyma; pb = phenolic body; rer = rough endoplasmic reticulum; ss = subcuticular space; va = vacuole; vs = vesicle. Scale bars A and B = 25 µm; C, D, G, J, K, and L = 2 µm; E and F = 5 µm; H = 1 µm; I = 0.5 µm.