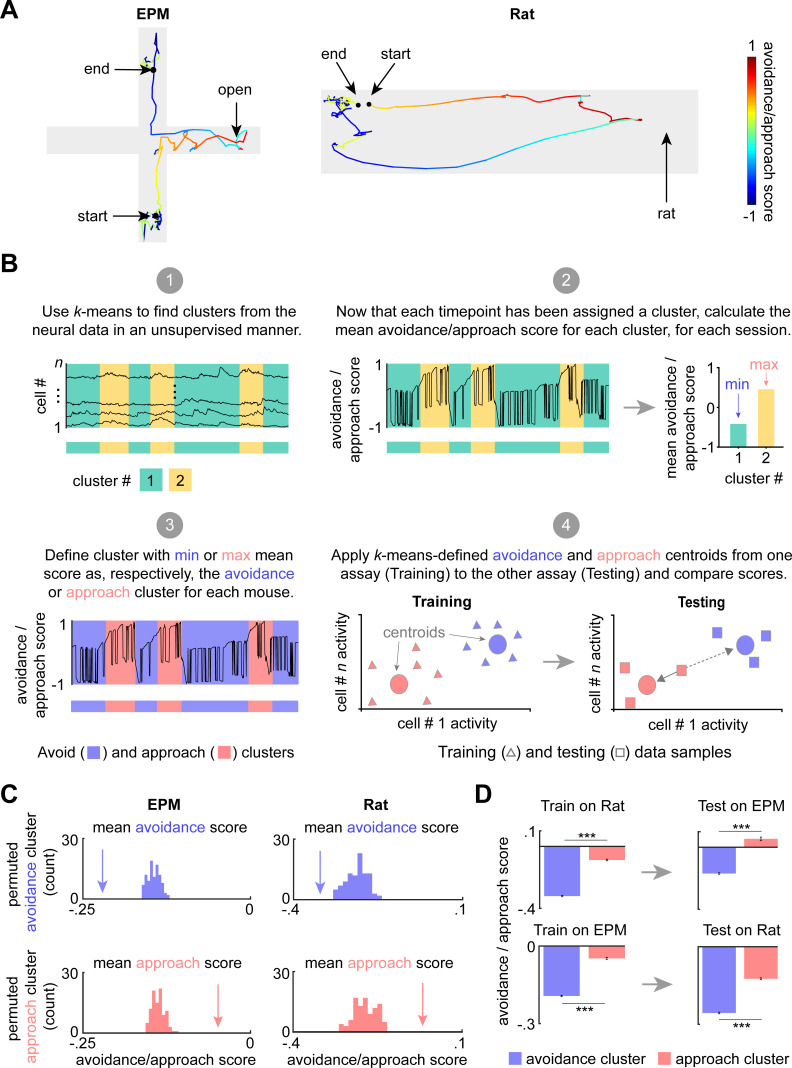
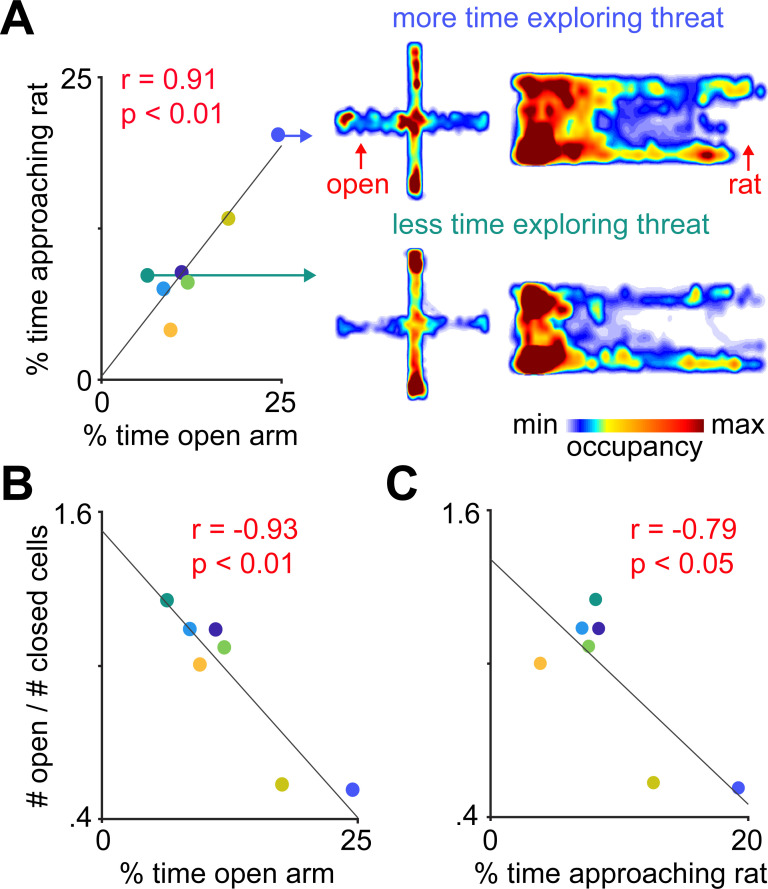
Figure 4. Dorsal periaqueductal gray (dPAG) displays a shared neural representation of avoidance and approach states across the elevated plus maze (EPM) and rat exposure assays.
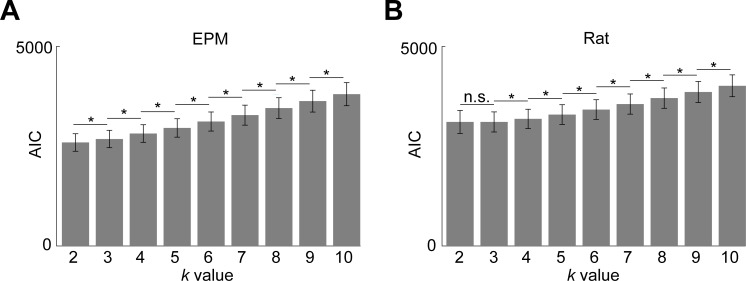
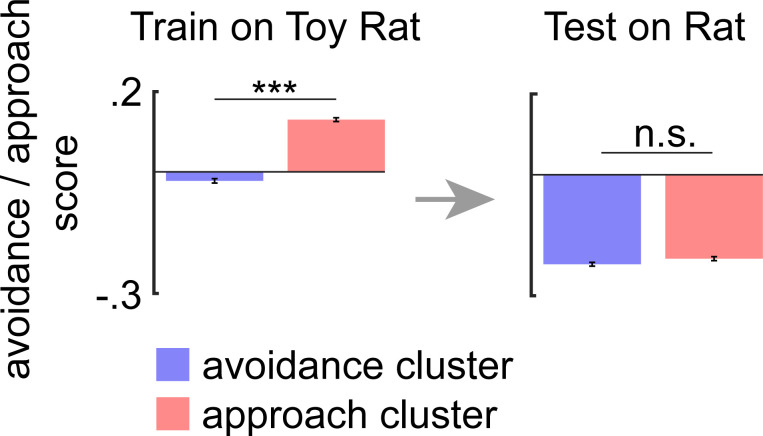
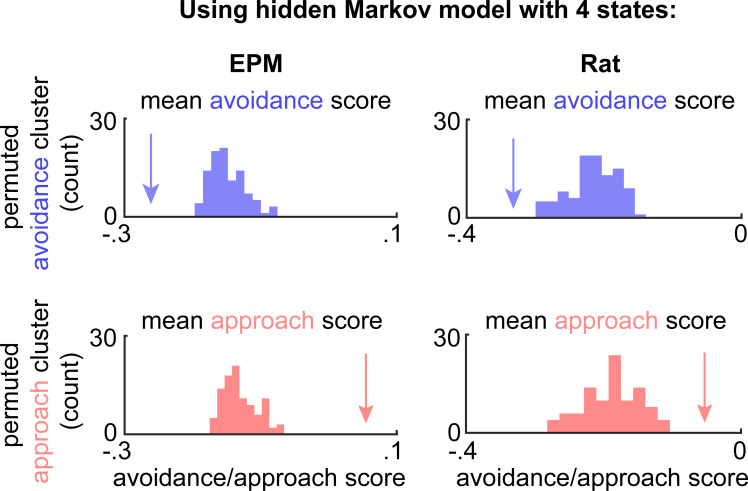
(A) Example tracks in the EPM (left) and rat exposure assay (right), color-coded by avoidance/approach score (see Materials and methods). The approach score increased during movements toward the threat, reaching +1 when the animal reaches the end of the open arms or the rat. The score decreases during movement away from threat and reaches its minimum value of −1 when the mouse reaches the end of closed arms or the furthest point from the rat. This score was developed as a measure of avoidance/approach states. (B) Explanatory diagram depicting steps of the clustering analysis (see Materials and methods). (1) k-Means was used to find clusters in the neural data in an unsupervised manner. (2) The mean avoidance/approach score was calculated for each cluster defined in step 1. (3) The ‘avoidance’ and ‘approach’ clusters were identified as those with, respectively, the minimum or maximum mean avoidance/approach score calculated in step 2. (4) The approach and avoidance centroids defined in one assay were used to classify neural data from the other assay, based on the minimum Euclidean distance for each sample (as depicted by solid arrow). (C) Arrow depicts the experimentally observed mean avoidance/approach score for avoidance and approach clusters (EPM k = 2; rat k = 3, see Figure 4—figure supplement 1) across concatenated sessions (n = 7 mice). This mean was compared to a distribution of avoidance (top) or approach (bottom) cluster means, calculated by permuting the neural data 100 times (EPM cells n = 734, rat assay cells n = 713; for all, p<0.01). (D) (Left) Bars depict the mean rat and EPM avoidance/approach scores (±1 SEM) for approach and avoidance clusters across mice. (Right) As described in Materials and methods and Figure 4B, these cluster centroid locations, trained on one assay, were then used to define approach and avoidance timepoints in the other assay. Bars depict the corresponding mean avoidance/approach score (±1 SEM) for this testing data (train on EPM: avoidance cluster n = 31,938, approach cluster n = 22,630; test on rat: avoidance cluster n = 30,245, approach cluster n = 24,412; train on rat: avoidance cluster n = 14,658, approach cluster n = 10,514; test on EPM: avoidance cluster n = 15,319, approach cluster n = 2510 (n represents the number of timepoints, not cells); co-registered cells n = 317; Wilcoxon rank sum test, ***p<0.001).