Fig. 5.
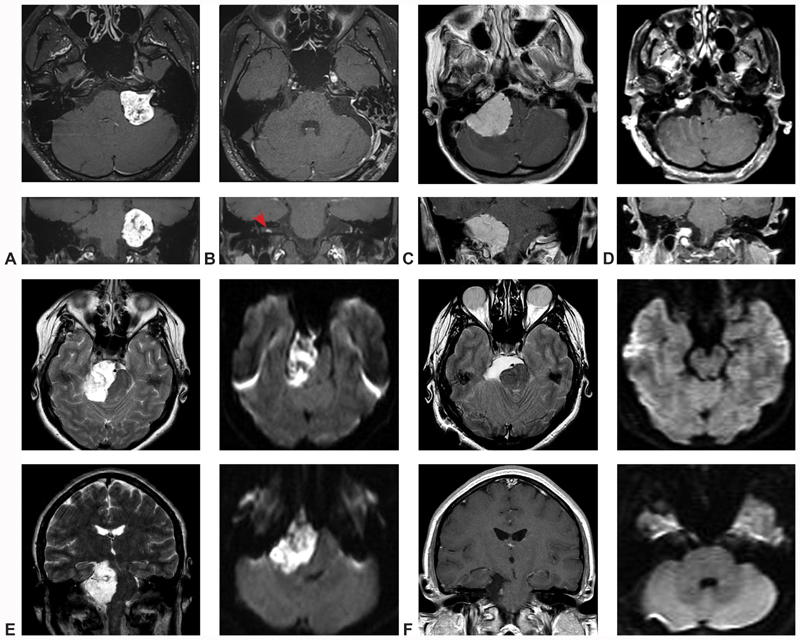
Illustrative cases. ( A – case one ) Preoperative T1-weighted MRI slices in the axial and coronal planes demonstrate a large, heterogeneous, vividly enhancing CPA mass with IAC extension, most consistent with vestibular schwannoma. ( B – case one ) Comparable postoperative T1-weighted MRI slices in the axial and coronal planes confirm gross total resection of the lesion, as well as a small, contralateral, intracanalicular mass, diagnostic of NF-II (red arrow). ( C – case two ) Preoperative T1-weighted MRI slices in the axial and coronal planes identify a very large, homogenously enhancing, dural-based CPA mass extending from the tentorium to the foramen magnum and causing severe compression and displacement of the brainstem, consistent with a jugular foramen meningioma. ( D – case two ) Following resection, a small, anticipated tumor residuum was noted at the jugular foramen, with aggressive subtotal resection of all other tumor. ( E – case three ) Preoperative T2-weighted axial and coronal MRI identified a very large hyper-intense CPA mass causing dramatic midbrain compression and mass effect. Diffusion-weighted sequences demonstrated marked restricted diffusion, confirming the diagnosis of epidermoid cyst. ( F – case three ) Postoperative T2-weighted axial, T1-weighted coronal, and diffusion-weighted axial and coronal sequences confirmed gross total resection of the lesion, with interval improvement in midline shift of the midbrain and pons. CN, Cranial nerve; CPA, cerebellopontine angle; IAC, Internal auditory canal; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; NF, neurofibromatosis.
