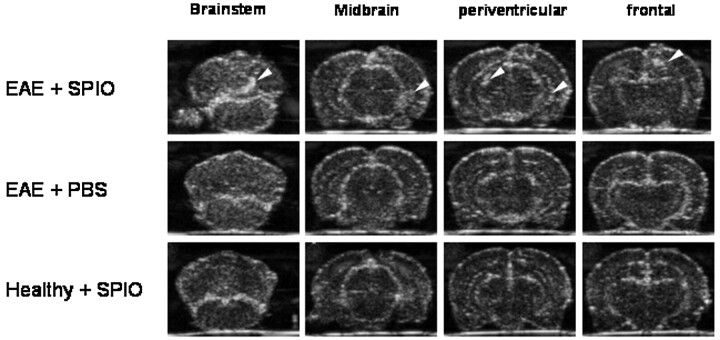
Fig 1.
SPIO-based macrophage imaging in EAE lesions of the rat brain by sonography. rhMOG-EAE was induced in congenic 1AV1 Lewis rats. During relapse, whole brains were removed and imaged ex vivo in a water tank by using a 13-MHz phased-array sonographic transducer 24 hours after SPIO injection. On coronal planes, sharply delineated circumscribed areas of focal echogenicity could be identified in different rats, predominantly involving the frontal, periventricular, cerebellar, and brain stem region (upper row, lesions marked by white arrows; representative images from different rats are shown), a pattern that is typical for MOG-EAE. Imaging of rat brains with injection of PBS after induction of rhMOG-EAE (middle row, anatomically equivalent areas from different rats are shown) or SPIO injection without prior induction of EAE (lower row) did not reveal similar areas with focal hyperechogenicity and served as negative controls.