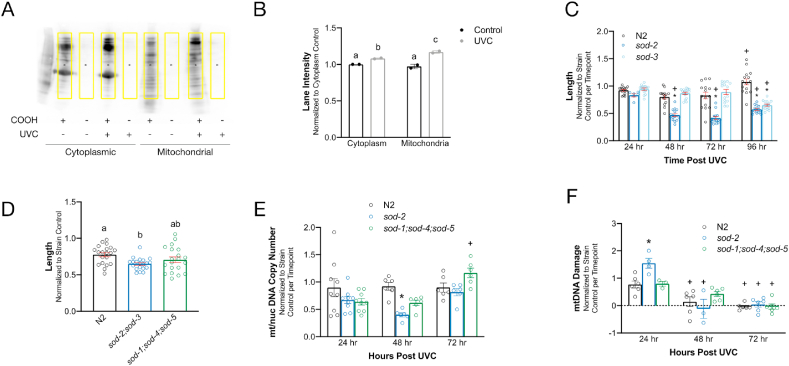
Fig. 5.
Mitochondrial SOD mutants are more sensitive to UVC exposure. A. Representative image of oxyblot at 4 days post-exposure demonstrates increased oxidative protein damage in UVC-exposed nematodes in both cytoplasmic and mitochondrial fractions. Yellow boxes indicate area of the blot that was quantified. COOH = derivatization reagent (required for detection), UVC = UVC exposure. B. Quantification of oxyblot. Error bars represent standard error. Letters show which groups are significantly different (p ≤ 0.05). Two-way ANOVA with Tukey's correction for multiple comparisons. n = 2 per group, 2 independent experiments. C.sod-2 and sod-3 mutants are more sensitive to UVC-induced growth delay 96 h post-exposure. Each UVC-exposed strain is normalized to its own non-exposed control at each time point. Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons (17 comparisons). n = 6–15 per group. *p ≤ 0.05 compared to N2 UVC-exposed at same time point. + p ≤ 0.05 compared to 24 h UCV exposed of same strain. D. The mitochondrial SOD double mutant sod-2;sod-3, is more sensitive to UVC-induced growth delay 72 h post UVC exposure than wild type N2 though the triple cytosolic and extracellular combination knockout (sod-1;sod-4;sod-5) is not. One-way ANOVA with Tukey's correction for multiple comparisons. n = 20 per group. Different letters indicate a significant difference (p ≤ 0.05) between groups E. mtDNA:nucDNA ratio in SOD mutants over time. Each UVC-exposed strain is normalized to its own non-exposed control at each time point. Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons (12 comparisons). n = 6–9 per group. *p ≤ 0.05 compared to N2 UVC-exposed at same time point. + p ≤ 0.05 compared to 24 h UVC exposed of same strain. F. mtDNA damage in SOD mutants. Each UVC-exposed strain is normalized to its own non-exposed control at each time point. mtDNA damage was increased by more than two-fold in UVC-treated sod-2 nematodes in comparison to both UVC-treated wild-type and sod-1;sod-4;sod-5 mutant nematodes at the 24 h timepoint. By 48 h and 72 h, damage levels had returned to our limit of detection in all strains. UVC-exposed sod-1;sod-4;sod-5 mutants were not statistically distinguishable from UVC-exposed N2s in terms of mtDNA damage at any timepoint. Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons (12 comparisons). n = 3–6 per group. *p ≤ 0.05 compared to N2 UVC-exposed at same time point. + p ≤ 0.05 compared to 24 h UVC-exposed of same strain. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)