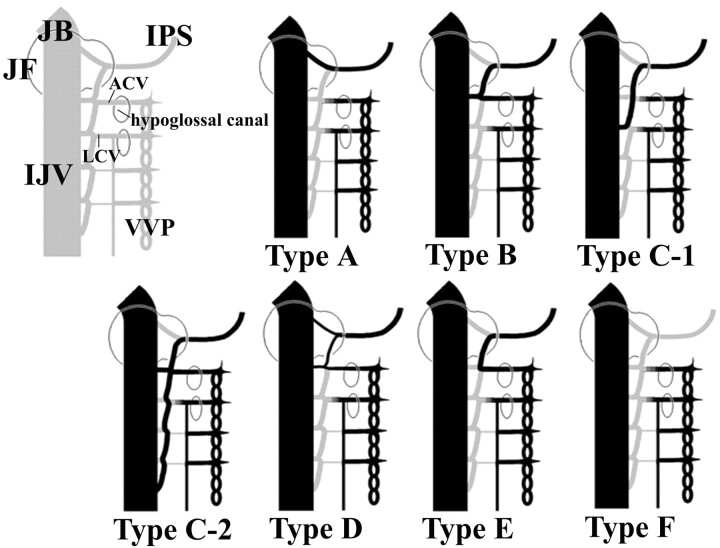
Fig 10.
The new classification is evaluated with our theory about the development of the caudal portion of the IPS.
In type A, the caudal portion of the IPS is derived from the vagal vein only and has no anastomosis with the VVP.
In type B, the caudal portion of the IPS is formed by the anastomosis of the vagal vein and the hypoglossal vein, so the anastomosis with the VVP via the ACV is common.
In type C-1, the caudal portion of the IPS is formed by the longitudinal anastomosis of the vagal vein, the hypoglossal vein, and the cervical intersegmental veins and drains into the extracranial lower IJV.
In type C-2, the upper venous route is formed as in type B, and the another lower route develops as in type C-1.
In type D, the development of the upper route drains is the same as that in type A, and the lower route develops as in type B.
In type E, no venous channel connecting the IPS to the IJV develops, and the venous return drains directly into the VVP via the venous route formed by anastomosis between the vagal vein and the hypoglossal vein.
In type F, the IPS is absent.