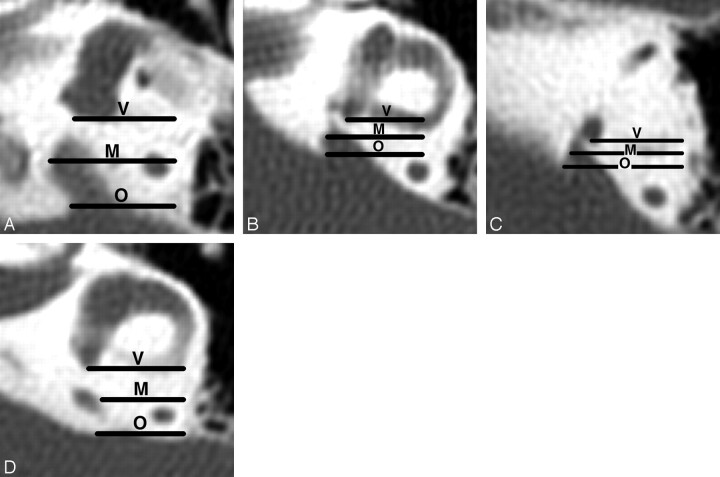
Fig 1.
Axial CT images showing the coronal planes used to define the VA midpoint plane in 4 temporal bones. The vestibular plane (V) lies at the level of the posterior wall of the vestibule or crus commune. The opercular plane is at the level of the VA operculum (O) or adjacent posterior wall of the petrous bone. The midpoint plane (M) is equidistant from the vestibular and opercular planes. Magnification of all images is the same. Enlarged rather than normal VAs are used for illustration so that the relationships of the VAs to the planes are easier to see.
A, The posterior wall of the vestibule defines the vestibular plane, and the edge of the operculum defines the opercular plane.
B, The transition between the posterior wall of the vestibule and crus commune defines the vestibular plane, and the edge of the operculum defines the opercular plane.
C, The posterior wall of the crus commune defines the vestibular plane, and the edge of the operculum defines the opercular plane.
D, The posterior wall of the vestibule defines the vestibular plane, and the posterior wall of the temporal bone just above the operculum defines the opercular plane.