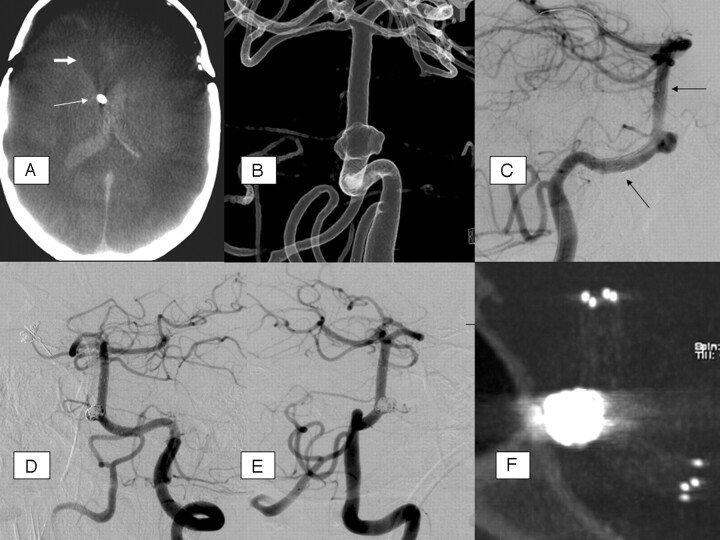
Fig 2.
A, Native, axial ACT-reconstruction, 5 mm section thickness; extensive SAH with intraventricular, hyperattenuated blood; CSF drainage adjacent to the septum pellucidum (arrow); previous frontal trepanation in the course of aneurysm clipping (anterior communicating artery); hypoattenuated brain parenchyma defect (thick arrow) with dilation of the frontal of the right lateral ventricle due to previous aneurysm rupture and parenchymal hemorrhage. B, Rotational 3D angiography with intra-arterial contrast agent injection, transparent surface shaded reconstruction (posterior-anterior view); broad-based proximal basilar stem aneurysm, forward oriented. The aneurysm base surrounds the basilar artery at least as a semicircle. C, DSA, lateral view; guidewire in the left posterior cerebral artery; Neuroform stent with proximal and distal markers (arrows). D and E, DSA (oblique views) after stent-assisted aneurysm coiling. F, MIP reconstruction of ACT after stent-assisted aneurysm coiling, providing excellent overview of the stent and the adjacent coil package; moderate beam-hardening artifacts.