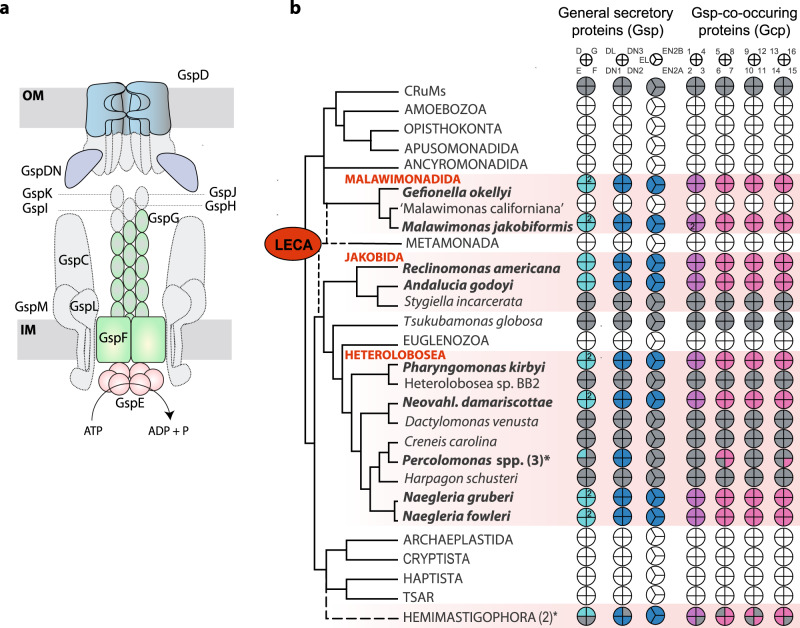
Fig. 1. Some eukaryotes harbour homologues of core components of the bacterial T2SS machinery.
a Schematic representation of the complete bacterial T2SS; subunits having identified eukaryotic homologues are highlighted in colour. For simplicity, GspDN represents in the figure three different eukaryotic proteins (GspDN1 to GspDN3), together corresponding to two versions of a conserved domain present as a triplicate in the N-terminal region of the bacterial GspD protein. b Phylogenetic distribution of eukaryotic homologues of bacterial T2SS subunits (Gsp proteins) and co-occurring proteins (Gcp). Core T2SS components (cyan), eukaryote-specific T2SS components (dark blue), Gcp proteins carrying protein domains found in eukaryotes (magenta) and Gcp proteins without discernible homologues or with homologues only in prokaryotes (pink). Coloured sections indicate proteins found to be present in genome or transcriptome data; white sections, proteins absent from complete genome data; grey sections, proteins absent from transcriptome data. The asterisk indicates the presence of the particular protein in at least two of the three Percolomonas or at least one of the two Hemimastigophora species analyzed. The species name in parentheses has not yet been formally published. Sequence IDs and additional details on the eukaryotic Gsp and Gcp proteins are provided in Supplementary Data 1. The tree topology and taxon names reflect most recent phylogenomic studies of eukaryotes;32, 101, 102 the root (LECA) is placed according to Derelle et al.29.