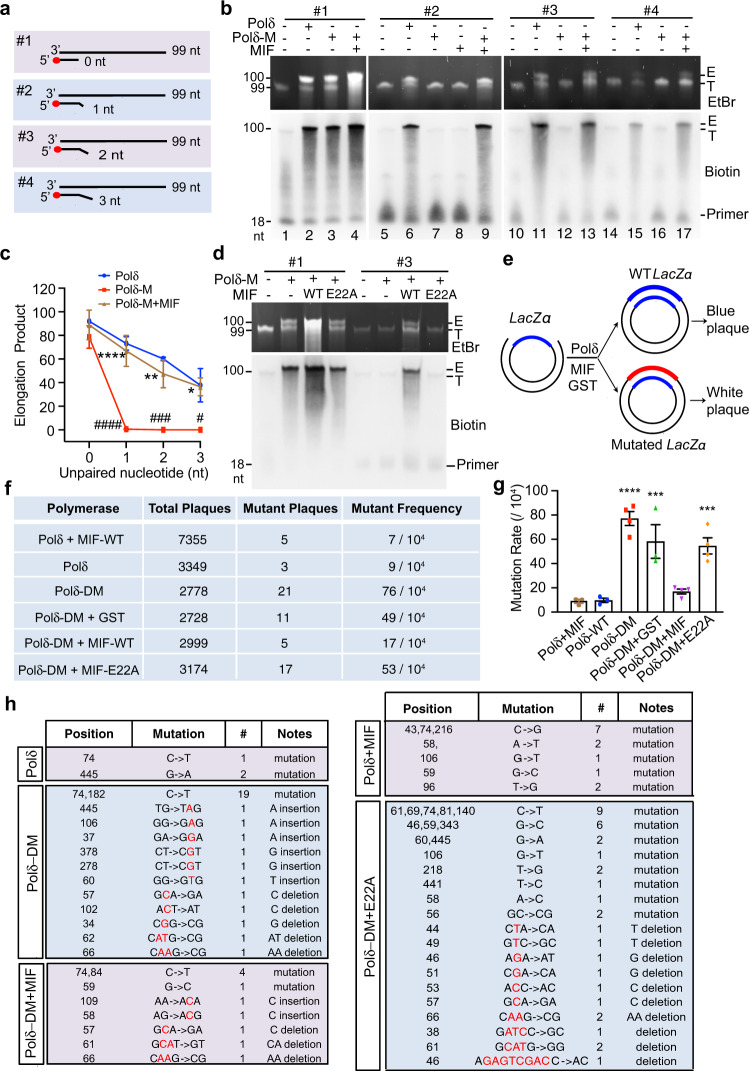
Fig. 2. MIF coordinates with the nuclease-deficient Pol δ D402A mutant to facilitate DNA elongation.
a Scheme of four types of 5’ biotin-labeled short DNA primers complementary to the template DNA without or with 1–3 nt mismatched nucleotides at the 3’ end for in vitro DNA elongation assay. b In vitro DNA elongation assay mediated by Pol δ or 3’ nuclease-deficient Pol δ D402A mutant (Pol δ-M) (5 ng/μl) in the presence or absence of MIF (2 μM) using a 99-bp DNA template (0.4 μM) and short primers (0.4 μM) listed in a. DNA was visualized by EtBr staining and Biotin immunoblot. E represents the elongation product. T indicates the complex of the 99-bp DNA template and biotin-labeled primer. c Quantification of in vitro DNA elongation assay in b (mean ± SEM, n = 3 biologically independent experiments). ####P < 0.0001, ###P < 0.001, #P < 0.05 Pol δ-M vs Pol δ; ****P < 0.0001, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05 Pol δ-M + MIF vs Pol δ-M; by two-way ANOVA Tukey’s multiple comparisons. d Effects of WT and E22A MIF (2 μM) on Pol δ-M-mediated DNA elongation using a 99-bp DNA template and #1 or #3 primer (0.4 μM). DNA was visualized by EtBr staining or biotin immunoblot. e Schematic diagram of DNA gap-filling synthesis by Pol δ or Pol δ D402A/L606M mutant (Pol δ-DM) (5 ng/μl) in the presence or absence of GST or MIF proteins (2 μM) and mutagenesis screening. f–h Mutation frequency and mutation sequence analysis of gap-filling assay mediated by Pol δ or Pol δ-DM in the presence of GST, WT MIF, or E22A MIF proteins. Mutation rate was quantified in g and presented as mean ± SEM. n = 3 biological replicates for Polδ + MIF, Polδ-WT and Polδ-DM + GST groups; n = 4 biological replicates for Polδ-DM, Polδ-DM + MIF, and Polδ-DM + E22A groups. ****P < 0.0001, ***P < 0.001 vs Polδ-WT, by one-way ANOVA Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. Source data are provided as Source Data file.