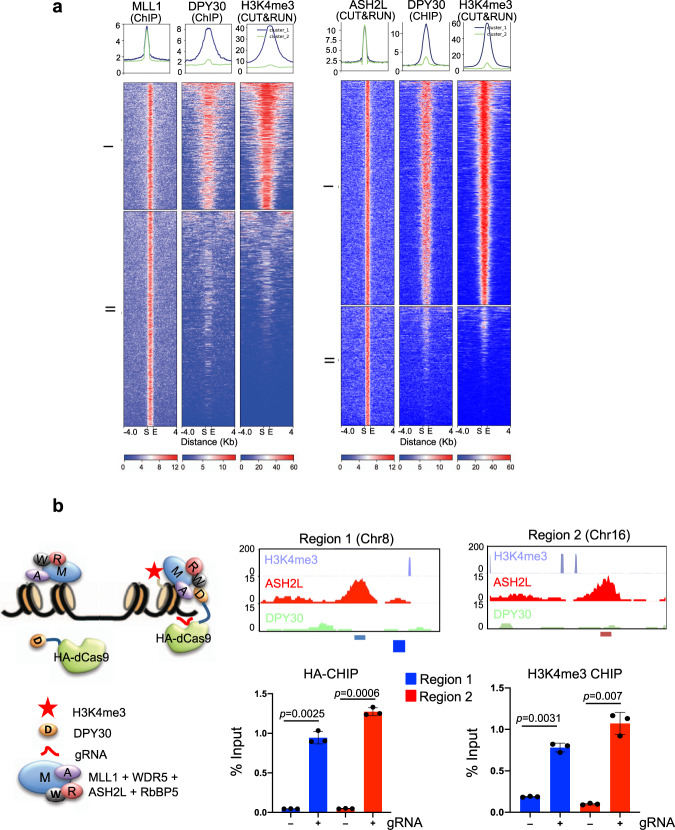
Fig. 6. DPY30 regulates de novo establishment of H3K4me3 on chromatin.
a DPY30 binding is highly correlated with H3K4me3 at the MLL1 binding sites. Heat map for 4009 MLL1 (left) and 2431 ASH2L (right) peaks and the corresponding DPY30 and H3K4me3 signals in ESCs. The signal as from merged biological duplicates. MLL1 or ASH2L peaks were clustered with K-means (K = 2) using normalized read counts at each peak. Two clusters were highlighted on left. Each row represents an 4 kb region up- and down-stream of the peak center. Peaks were sorted based on normalized read counts in each cluster. b DPY30 is able to establish de novo H3K4me3 on chromatin. Left, Experimental design for gRNA-mediated recruitment of dCas9-DPY30. The dCas9-DPY30 is recruited by gRNA to chromatin loci with prior binding of ASH2L and MLL1 and promotes H3K4me3 on chromatin. In the absence of gRNAs, dCas9-DPY30 is not recruited to target loci. W, WDR5; R, RbBP5; A, ASH2L; M, MLL1; D, DPY30. Right top, UCSC browser views of two randomly selected genomic regions are bound by ASH2L, but not DPY30. These regions do not have prior H3K4me3. Regions for gRNAs were highlighted on bottom. Right bottom, ChIP assay for HA-dCas9-DPY30 (left) or H3K4me3 (right) in cells transfected with or without the pooled gRNAs. ChIP signals were normalized against input and presented as %Input. Means and standard deviations (error bars) from at least three independent experiments were presented. Two-sided student t test was performed to calculate p-value.