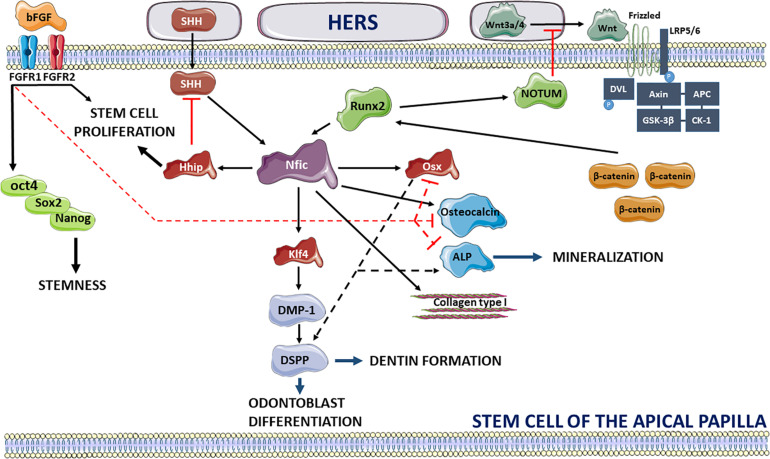
FIGURE 2.
Overview of signaling pathways regulating the stemness of SCAP and promoting dental root development via extrinsic signals of HERS. bFGF maintains the stemness of SCAP via activation of FGFR1 and 2 promoting expression of stemness factors oct4, Sox2, and Nanog, inhibits mineralization through interaction with Osx, Osteocalcin, and ALP and promotes cell proliferation. HERS stimulates dental root maturation by secretion of Wnt3a and Wnt4 interacting with the Frizzled and LRP5/6 receptors. Activation of Wnt signaling acts via binding and phosphorylation of DVL, phosphorylation of LRP5/6 and de-activation of the Axin, APC, GSK-3β, and CK-1 complex leading to inhibition of β-catenin degradation. Consequently, β-catenin interacts with Runx2 activating the Nfic pathway. Nfic triggers odontoblast differentiation and dentin formation by acting with Klf4 and promoting DMP-1 and DSPP expression. Secondly, Nfic induces mineralization by upregulating Osteocalcin, ALP and collagen type I and through interaction with Osx which promotes ALP production and DSPP expression. Alternatively, HERS activates Nfic signaling independent of Runx2 via secretion of SHH. Wnt and hedgehog signaling pathways are, respectively, antagonized by Runx2-driven secretion of NOTUM and Nfic-promoted expression of Hhip which promotes stem cell proliferation. Activators of signaling pathways are shown in black lines (full and dotted) whereas inhibition is depicted in red. This image was created using Servier Medical Art, licensed under a Creative Common Attribution 3.0 Generic License, available online at https://smart.servier.com/.