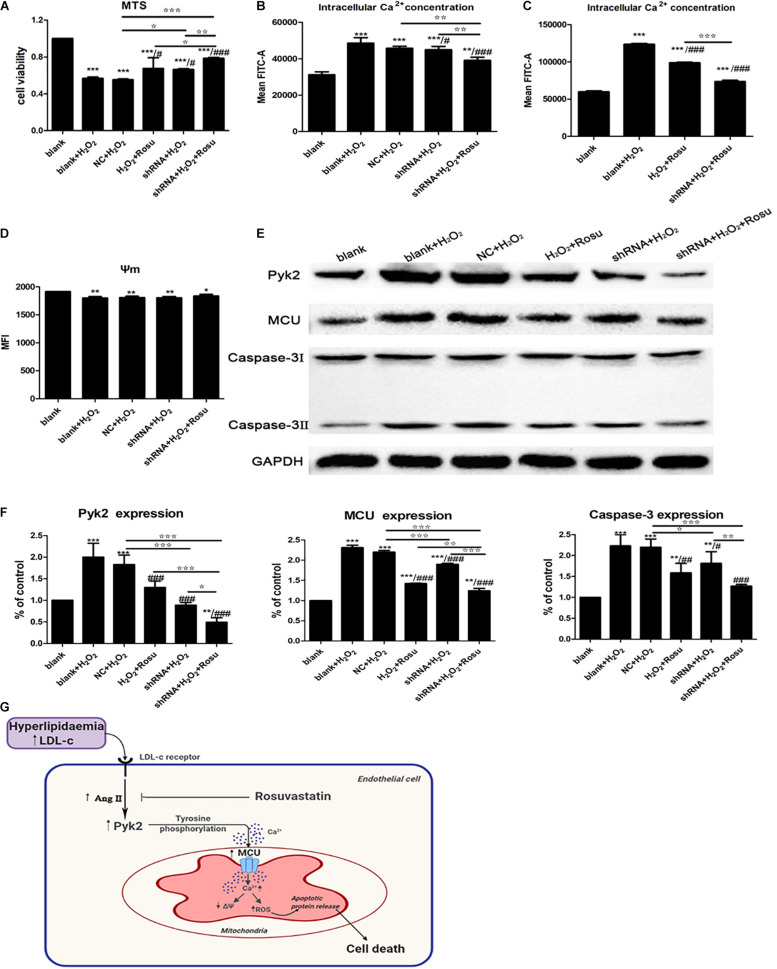
FIGURE 8.
The effect of Pyk2 down-regulation on H2O2-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) injury and regulation of the Pyk2/mitochondrial calcium uniporter (MCU) pathway in endothelial cell. (A) Detection of cell viability by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-5-(3-carboxymethoxyphenyl)-2-(4-sulfophenyl)- 2H-tetrazolium assay after transfection with shRNA. (B–D) Detection of intracellular free Ca2+ and mitochondrial membrane potential in different groups by flow cytometry. (E) Pyk2, MCU, and caspase-3 protein expression in different groups by western blot. (F) Statistical graph of panel (E). Data are shown as mean ± SD of at least three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 versus vehicle blank group (control); #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001 versus vehicle H2O2 group (blank+H2O2); ✩P < 0.05, ✩✩P < 0.01, ✩✩✩P < 0.001, NC+H2O2 vs. shRNA+H2O2, NC+H2O2 vs. shRNA+H2O2+Rosu; H2O2+Rosu vs. shRNA+H2O2+Rosu, shRNA+H2O2 vs. shRNA+H2O2+Rosu, one-way ANOVA. (G) Endothelial angiotensin II involvement-Pyk2-dependent MCU phosphorylation initiates mitochondrial Ca2+ entry, which, in turn, induces reactive oxygen species generation and a decrease in mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP/ΔΨ) and eventually leading to cell death.