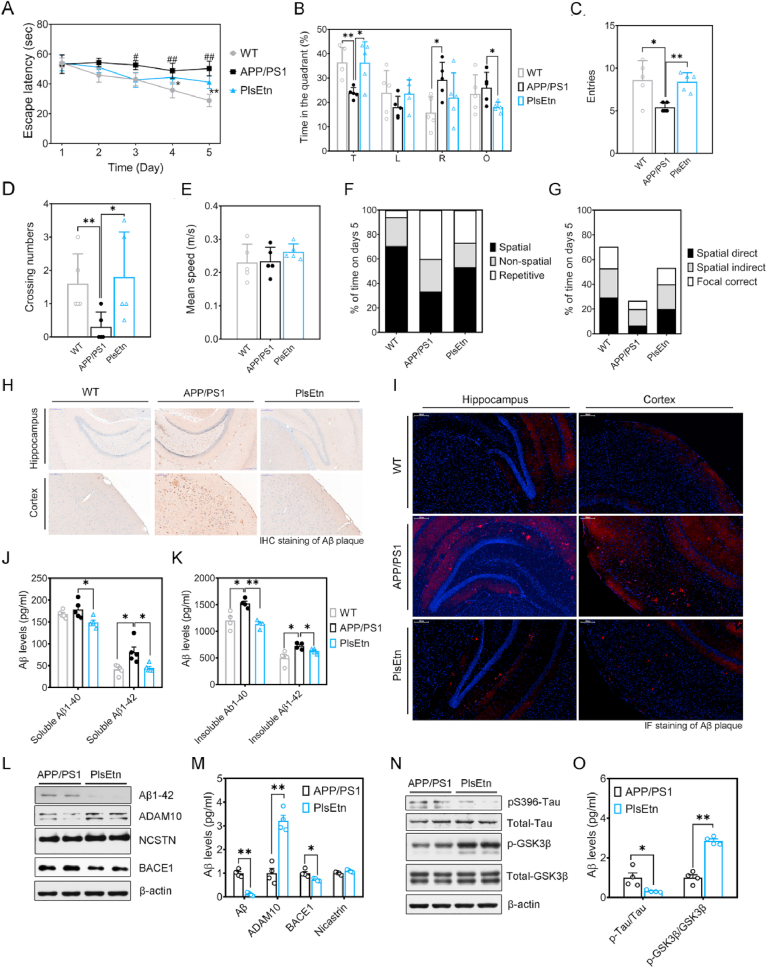
Fig. 5.
PlsEtn supplementation ameliorates memory deficits, Aβ and Tau pathology. (A) Escape latency to the platform during the training trails in a Morris water maze (n = 5 mice/group). (B) Time spent in target quadrant in the MWM test at day 5. (C) Times crossing the target sites after retrieval of the platform at day 5. (D) Entries in target quadrant. (E) Average speed to find the platform. (F) Assessment of search strategy (spatial, non-spatial, repetitive) in the acquisition phase of the water maze test. (G) The percentage of time engaged in spatial search strategies during the 60-s trial was calculated, with search strategies combined into 3 groups based on functional similarity (Spatial Direct, Spatial Indirect, and Focal Correct strategies). (H and I) Photomicrographs of Aβ plaques within the hippocampus of APP/PS1 and PlsEtn-fed mice (n = 6 mice/group). Scale bar, 200 μm. (J and K) Quantitative analysis for the soluble and insoluble forms of Aβ1-40 and Aβ1-42 in hippocampus of APP/PS1 mice (n = 6 mice/group). (L and M) Representative Western blot of APP processing. (N and O) Representative Western blot of tau and p-Tau. Statistical significance was determined by Student's t-test, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 vs APP/PS1 mice; #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01 vs WT mice.