Figure 3.
Determining the quality of a step fit
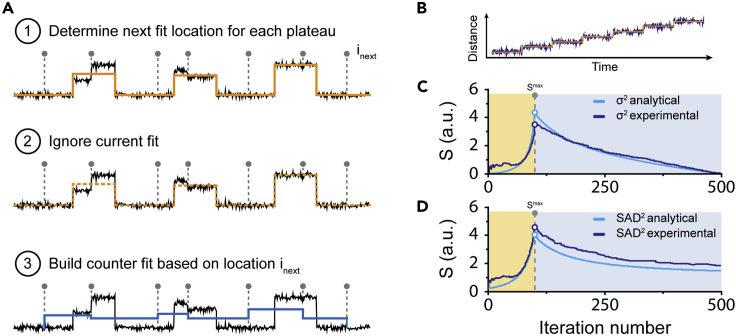
(A) For every step fit the algorithm performs, the quality of the fit (orange line) is evaluated by means of an additional fit (blue line, called a counter fit). The counter fit is built by determining the next partition point (inext), after which the current is rejected. Subsequently, the algorithm places the counter fit (blue) plateaus at locations within the existing fit (orange).
(B) Simulated trajectory representing a motor stepping behavior.
(C) Representative example of experimental and analytical S-curves obtained by fitting the trajectory in (B) through minimization of σ2. Shaded areas indicate the underfitting (yellow) and overfitting (light blue) regime.
(D) Representative example of experimental and analytical S-curves obtained by fitting the trajectory in (B) through minimization of the sum of absolute differences (SAD2). Shaded areas indicate the underfitting (yellow) and overfitting (light blue) regime.
Also see Figure S2.