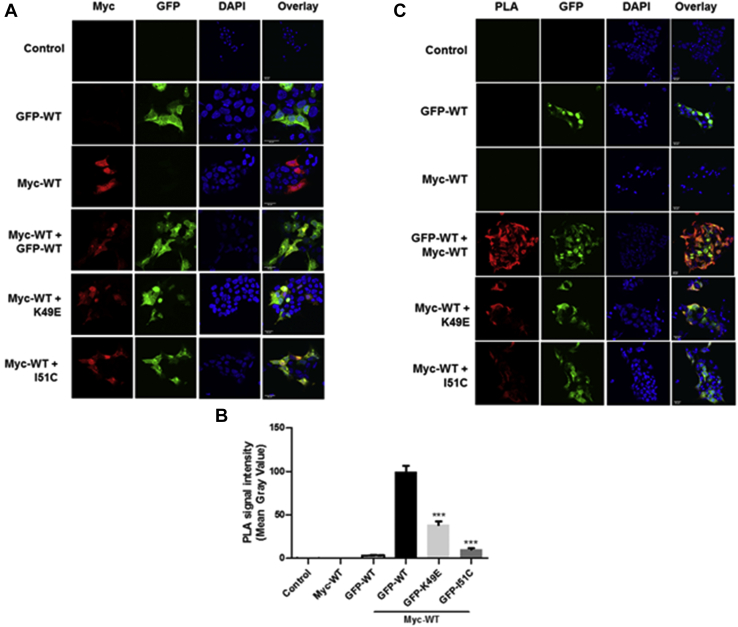
Figure 8.
Duolink PLA for protein interaction detection between WT Myc-mSK1 and WT GFP-mSK1, K49E GFP-mSK1, or I51C GFP-mSK1 in MCF-7L cells.A, MCF-7L cells overexpressing WT Myc-mSK1 with WT GFP-mSK1, K49E GFP-mSK1, or I51C GFP-mSK1 was confirmed by fluorescence microscopy before Duolink PLA to assess protein interactions. PLA was carried out to assess differences in protein interaction between WT Myc-mSK1 and WT GFP-mSK1 or K49E GFP-mSK1 or I51C GFP-mSK1 when coexpressed. Untransfected cells (control) and cells expressing only WT GFP-mSK1 or WT Myc-mSK1 were used as negative controls. Cells were processed for PLA and mounted with DAPI to stain the DNA (blue). B, quantitative analysis of the cellular PLA signals was carried out. The bar graphs represent the PLA signal mean gray value (mean ± SEM) with experiments carried out in triplicate (50 cells total per sample group shown) ∗∗∗p < 0.001 for WT Myc-mSK1/mutant GFP-mSK1 combination versus WT Myc-mSK1/WT GFP-mSK1 combination (one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test). C, representative PLA images are shown. The scale bar represents 20 μm. mSK1, mouse SK1; PLA, proximity ligation assay.