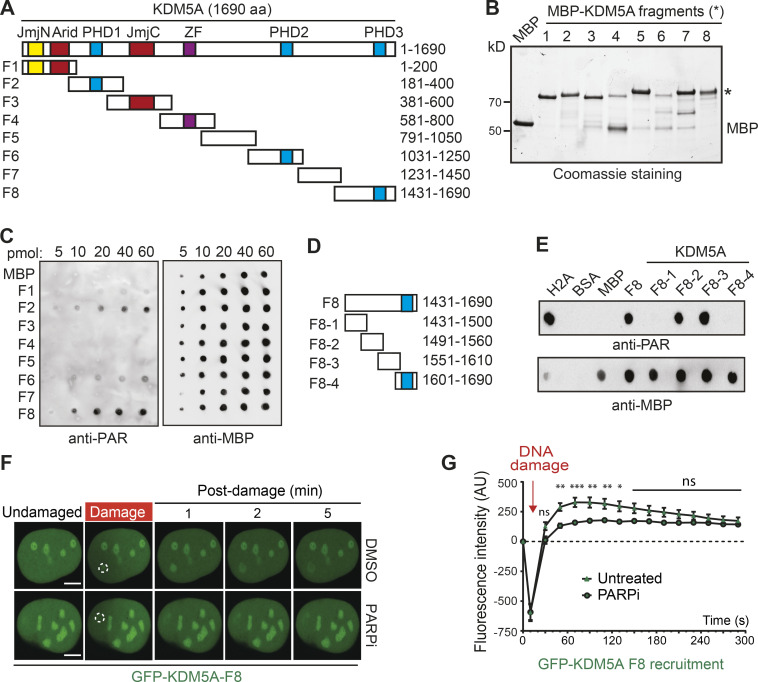
Figure 3.
Mapping of a PAR interaction domain within KDM5A. (A) Domain organization of KDM5A. Schematics for overlapping KDM5A fragments (F1–F8) are indicated. (B) Expression of affinity-purified, MBP-tagged KDM5A fragments. Purified fragments were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining. (C) Purified MBP and MBP-KDM5A fragments F1–F8 were analyzed for PAR binding as in Fig. 2 F. (D) Schematics for KDM5A-F8 and derivatives. Blue box indicates PHD3 domain. (E) PAR binding resides in KDM5A-F8-2 and F8-3. PAR binding was performed as in C with indicated proteins. (F) GFP-KDM5A-F8 sufficient for PARP-dependent recruitment to laser damage. Laser microirradiation was performed in U2OS cells transfected with GFP-KDM5A-F8 with or without the PARPi olaparib (5 µM, 1 h). Damaged region is indicated by dotted white circle. Scale bars, 5 µm. (G) Quantification of F from two representative experiment where n ≥ 20 cells. Error bars represent SEM. P values were calculated with unpaired Student’s t test (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001).