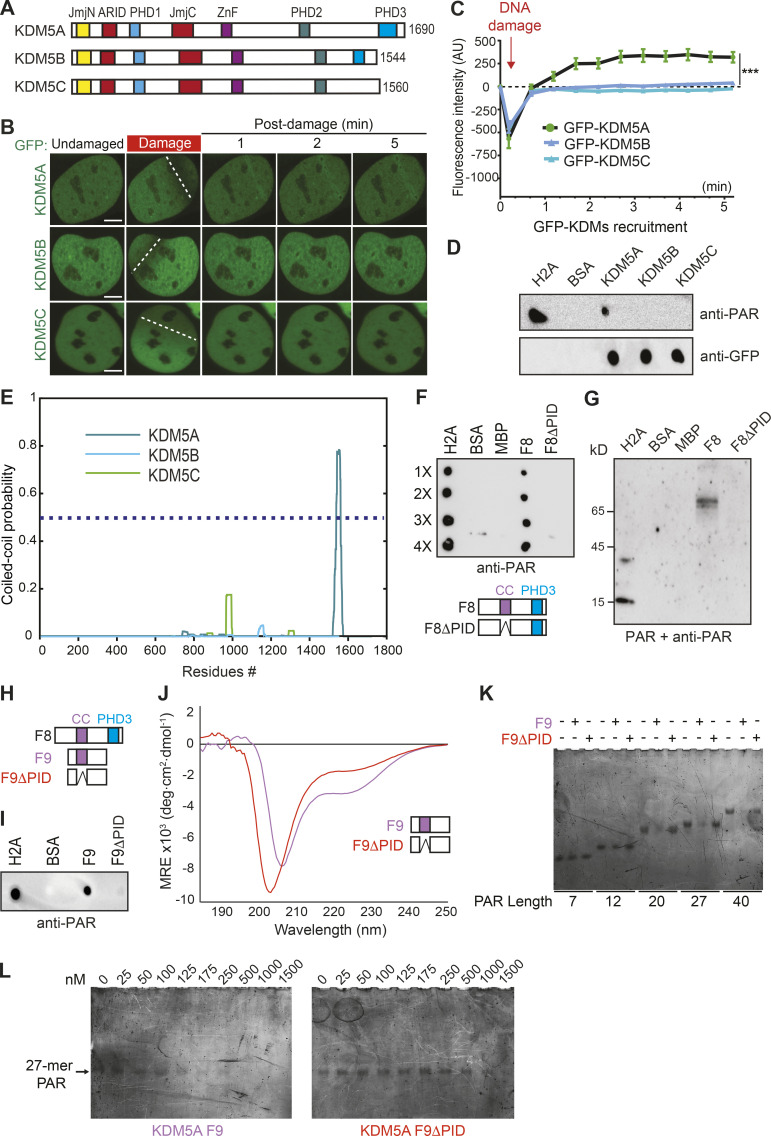
Figure 4.
KDM5A contains a coiled-coil domain that facilitates preferential binding to longer PAR chains. (A) Schematic of human KDM5A, KDM5B, and KDM5C. (B) Recruitment of GFP-KDM5A, GFP-KDM5B, and GFP-KDM5C to laser-induced DNA damage sites using live-cell confocal microscopy and laser microirradiation. White dotted lines indicate path of laser damage. Scale bars, 5 µm. (C) Quantification of B from one representative experiment. n > 7 individual cells per condition. Two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparison test was used for statistical analysis comparing KDM5A with KDM5B and KDM5C recruitment. Error bars represent SEM (***, P < 0.001). (D) KDM5A uniquely interacts with PAR chains. GFP-tagged KDM5A, KDM5B, and KDM5C were expressed and purified from U2OS cells. PAR binding was performed as in Fig. 2 F. (E) KDM5A contains a predicted coiled-coil region that is absent from KDM5B and KDM5C. Predicted per residue coiled-coil scores for dimers were calculated using MultiCoil (see Materials and methods). (F) KDM5A region predicted as a coiled-coil (residues 1501–1562) is required for PAR binding (PID). PAR-binding assay performed as in D. Diagram of KDM5A-F8 and KDM5A-F8ΔPID with putative coiled-coil (cc) and PHD3 domains indicated. (G) Far-WB analysis of KDM5A PAR binding. The indicated proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE and blotted onto a nitrocellulose membrane. The membrane was incubated with PAR chains, and the indicated proteins were detected as in D. (H) Comparative diagram of KDM5A-F8 with KDM5A-F9 (1491–1610) and KDM5A-F9ΔPID (1491–1610Δ1501-1562). (I) PAR-binding analysis of KDM5A-F9 and KDM5A-F9ΔPID. PAR binding assay was performed as in D. (J) CD spectrum for the F9 region of KDM5A-F9 (purple) is consistent with the presence of α-helical protein elements, while the CD spectrum for F9ΔPID (1491–1610Δ1501-1562; red) exhibits an appreciable loss in this helicity, supporting the predictive model of a coiled-coil domain between residues 1501 and 1562. Notably, both KDM5A-F9 and F9ΔPID harbor significant intrinsically disordered protein regions. deg, degree; MRE, mean residue ellipticity. (K) KDM5A-F9, but not F9ΔPID, has preferential nM binding for medium and long PAR chains. (L) EMSA titrations demonstrate that KDM5A-F9 has nM binding for a medium-length 27-mer PAR chain, while PAR recognition by F9ΔPID is severely compromised.