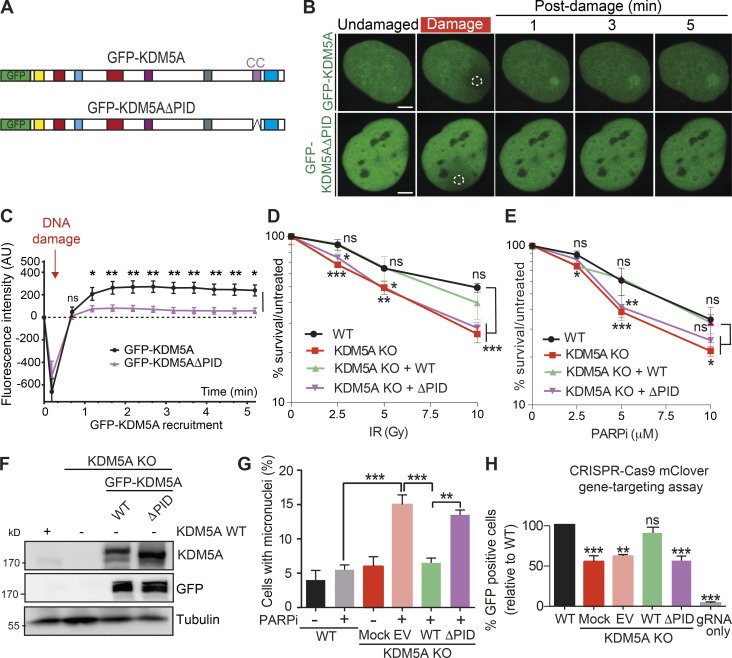
Figure 5.
The PID containing a coiled-coil region is required for damage localization and DDR functions of KDM5A. (A) Diagram of KDM5A constructs used in B. (B) KDM5A-PID is required for damage localization. Experiments were performed as in Fig. 3 F. Damaged regions are indicated by dotted white outlines. Scale bars, 5 µm. (C) Quantification of B from one representative experiment. Error bars represent SEM; n ≥ 10 cells. Damaged regions are indicated by a dotted white line. (D and E) KDM5A-PID is required for survival in response to IR and PARPi. Clonogenic survival assays were performed as in Fig. 1 A with the indicated ectopically expressed KDM5A genes. Error bars represent SD; n = 3. (F) WB analysis of WT and KDM5A-KO HCT116 cells, including GFP-KDM5A WT and ΔPID reconstituted cells. (G) KDM5A-PID suppresses micronuclei formation. Experiments were performed as in Fig. 1 C with the indicated KDM5A-KO cells and complemented cells as in D. Error bars represent SD; n = 2. P values were calculated by Tukey’s multiple comparison test (**, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001). (H) KDM5A-PID is required for efficient homology-directed repair (HDR). HDR efficiency in HCT116 WT and KDM5A-KO cells with or without SFB-KDM5A and SFB-KDM5AΔPID was determined using a CRISPR-mClover HR assay. GFP+ cells represent a repair event. The percentage of GFP+ cells was normalized to WT. Error bars represent SEM; n = 2. P values were calculated for C, D, E, and H with unpaired Student’s t test (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001).