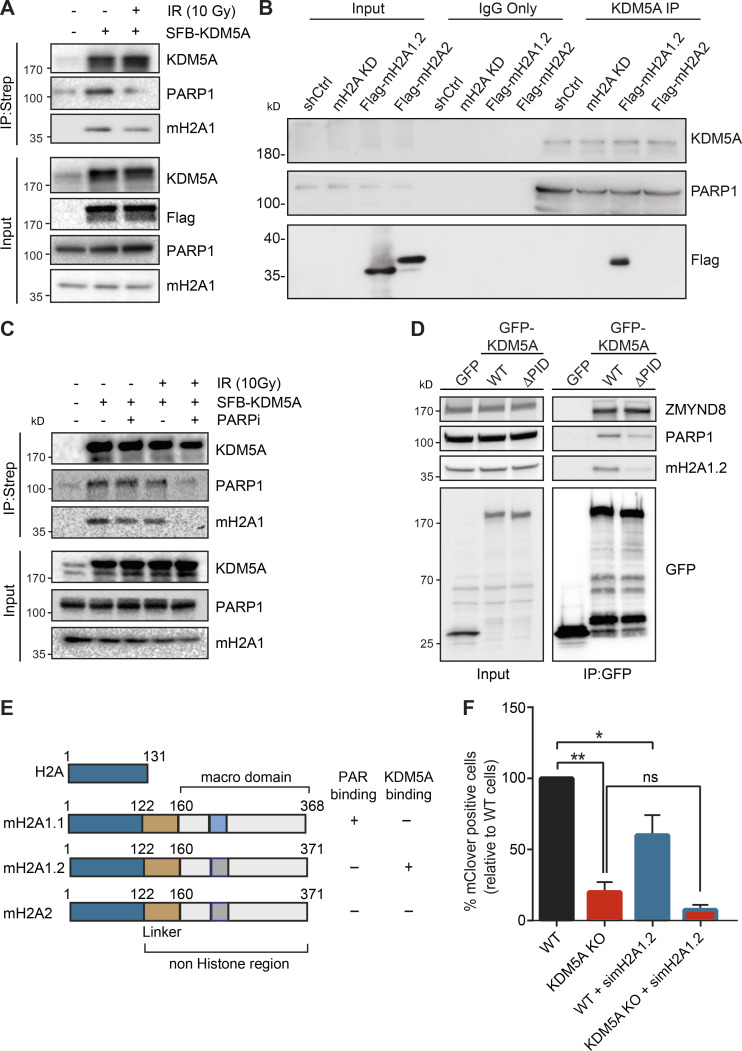
Figure 6.
KDM5A interacts with the histone variant macroH2A1.2. (A) KDM5A interacts with macroH2A1. Inducible SFB-KDM5A–expressing HEK293T cells were treated with or without 10-Gy IR. SFB-KDM5A was immunoprecipitated with streptavidin beads, and interactions were detected by WB analysis. Input shows expression and loading of proteins. (B) Endogenous KDM5A interacts with macroH2A1.2. Co-IPs were performed using HepG2 cells depleted with shRNA control (shCtrl) or shRNA macroH2A (mH2A knock down [KD]) and complemented shRNA-macroH2A with Flag-macroH2A1.2 or Flag-macroH2A2. (C) KDM5A and macroH2A1.2 interactions are PARP dependent. SFB-KDM5A–expressing HEK293T cells were treated with DMSO or olaparib (5 µM, 1 h) with or without subsequent 10-Gy IR treatments. Co-IPs were performed as in A. (D) The PID of KDM5A is required for macroH2A1.2 and PARP1 interactions. HEK293T cells expressing GFP, GFP-KDM5A, or GFP-KDM5AΔPID were analyzed by co-IP WB analysis with the indicated antibodies. (E) Comparison of domain structure of histone H2A and macroH2A variants with PAR- and KDM5A-binding summary. Dark blue represents a highly conserved region between canonical H2A and macroH2A variants; gold represents a linker region; light blue represents the PAR-binding region within the macrodomain; dark gray represents a region that has lost PAR binding. (F) KDM5A and macroH2A1.2 promote HDR. Measurement of HR efficiency in WT and KDM5A-KO cells with or without siRNA depletion of macroH2A1.2 was performed as in Fig. 5 H (n = 2). Error bars represent SEM. P values were calculated using an unpaired Student’s t test (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01).