FIGURE 6.
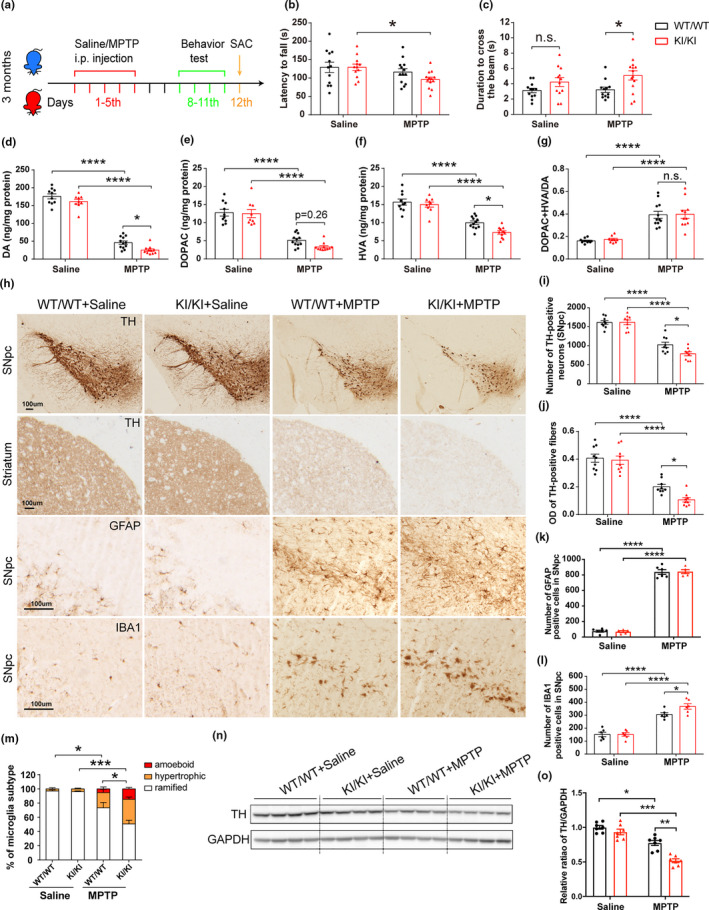
Increased MPTP vulnerability of VPS35 D620N KI mice. (a) A schematic diagram depicts the experimental design. (b–c) Exacerbated motor function deficits in VPS35D620N / D620N mice as measured by the latency to fall in rotarod test (b) and duration to cross the narrow beam (9 mm) in beam walking test (c) (n = 12–14/group). (d–g) Concentrations of DA (d), DOPAC (e), HVA (f), and DA turnover rate (DOPAC+HVA/DA) (g) in the STR of VPS35D620N / D620N and WT controls injected with MPTP/Saline as indicated (n = 10–12/group). (h) Representative images of TH, GFAP, and IBA1 immunostaining in SNpc and STR from VPS35D620N / D620N and WT mice injected with MPTP/Saline as indicated. Scale bar, 100 μm. Quantification of TH‐positive neurons in SNpc (i), OD of TH‐positive fibers in STR (j), GFAP‐positive cells (k) and IBA1‐positive cells (l,m) in SNpc (n = 9/group). Representative Western blots (n) and quantification (o) of TH in VM extracts from VPS35D620N / D620N mice and WT controls injected with MPTP/Saline as indicated (n = 7/group). Two‐way ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test; mean ± SEM; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, n.s., not significant
