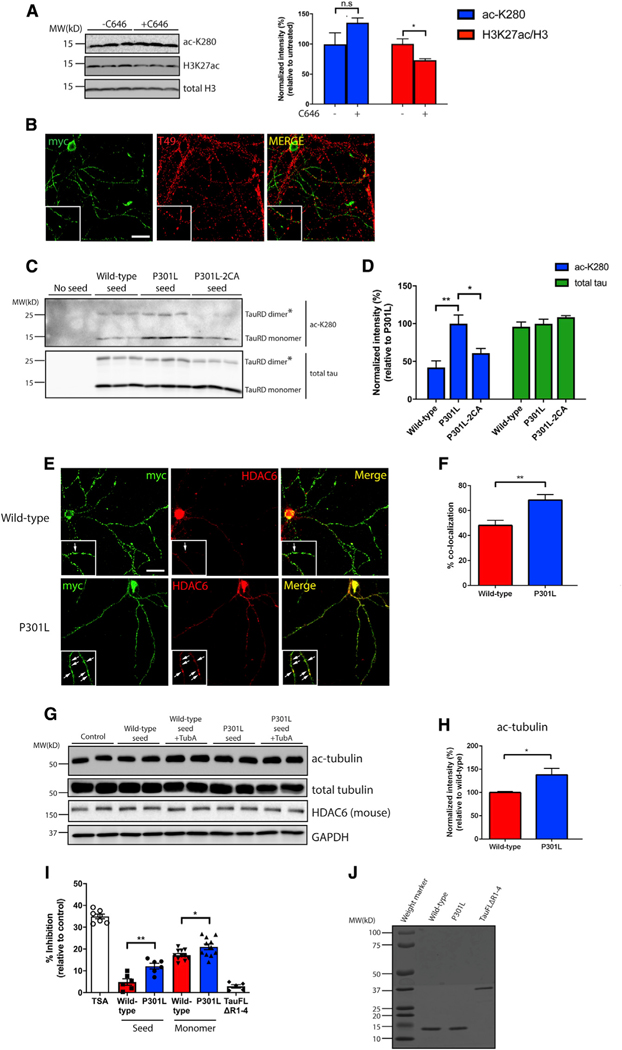
Figure 5. Tau seeds undergo auto-acetylation and inhibit HDAC6 activity.
(A) Primary neurons were exposed to P301L tau seeds in the presence or absence of a CBP/p300 inhibitor, C646 (20 μM), followed by immunoblotting with acetylated tau (ac-K280), H3K27ac, and total H3 antibodies. Acetylation of tau and H3K27 were quantified on the right. Error bars indicate SEM; n = 3 biologically independent experiments. P value was determined by unpaired t test. n.s. p > 0.05, *p < 0.05.
(B) Primary neurons were exposed to myc-tagged P301L tau seeds and analyzed by double labeling with the mouse tau-specific T49 antibody (red) in combination with myc antibody (green) to illustrate minimal co-localization between endogenous mouse tau and tau seeds. Scale bar, 50 μm.
(C) Primary neurons were exposed to WT, P301L, or P301L/C291A/C322A (P301L-2CA) seeds followed by immunoblotting with acetylated (ac-K280) and total tau antibodies. The asterisks (*) highlight tau dimers. Double cysteine mutants (P301L-2CA) are partly deficient in tau auto-acetylation.
(D) Quantification of tau acetylation among WT, P301L, and P301L-2CA seeds. Error bars indicate SEM; n = 3 biologically independent experiments. p value was determined by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s test for multiple comparisons among groups. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.
(E) Primary neurons were exposed to myc-tagged WT or P301L tau seeds and analyzed by double-labeling with myc antibody (green) in combination with a mouse HDAC6 antibody (red). Co-localization is highlighted by arrows in the inset. Scale bar, 50 μm.
(F) Quantification of co-localization was determined as percent tau seed co-localization among total tau seeds. Error bars indicate SEM; n = 4 biologically independent experiments. p value was determined by unpaired t test. **p < 0.01.
(G) Primary neurons were exposed to WT or P301L tau seeds in the absence or presence of tubastatin A (TubA; 1 μM) followed by immunoblotting with ac-tubulin, total tubulin, and HDAC6 antibodies. GAPDH served as a loading control.
(H) Quantification of ac-tubulin normalized to total tubulin levels in neurons exposed to WT or P301L tau seeds. Error bars indicate SEM; n = 4 (WT) or 5 (P301L) biologically independent experiments. P value was determined by unpaired t test. *p < 0.05.
(I) An HDAC6 in vitro activity assay was used to evaluate the inhibitory capability of WT or P301L monomers and seeds. Trichostatin (TSA) and full-length tau lacking the MTBR (tauFLΔR1–4) served as positive and negative controls, respectively. The different inhibitory capabilities between tau species were analyzed. Error bars indicate SEM; n = 4 (WT seed and P301L seed), 5 (tauFLΔR1–4), or 7 (TSA, WT monomer, and P301L monomer) biologically independent experiments. p value was determined by unpaired t test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.
(J) Coomassie blue staining of WT, P301L, and tauFLΔR1–4 recombinant tau proteins.