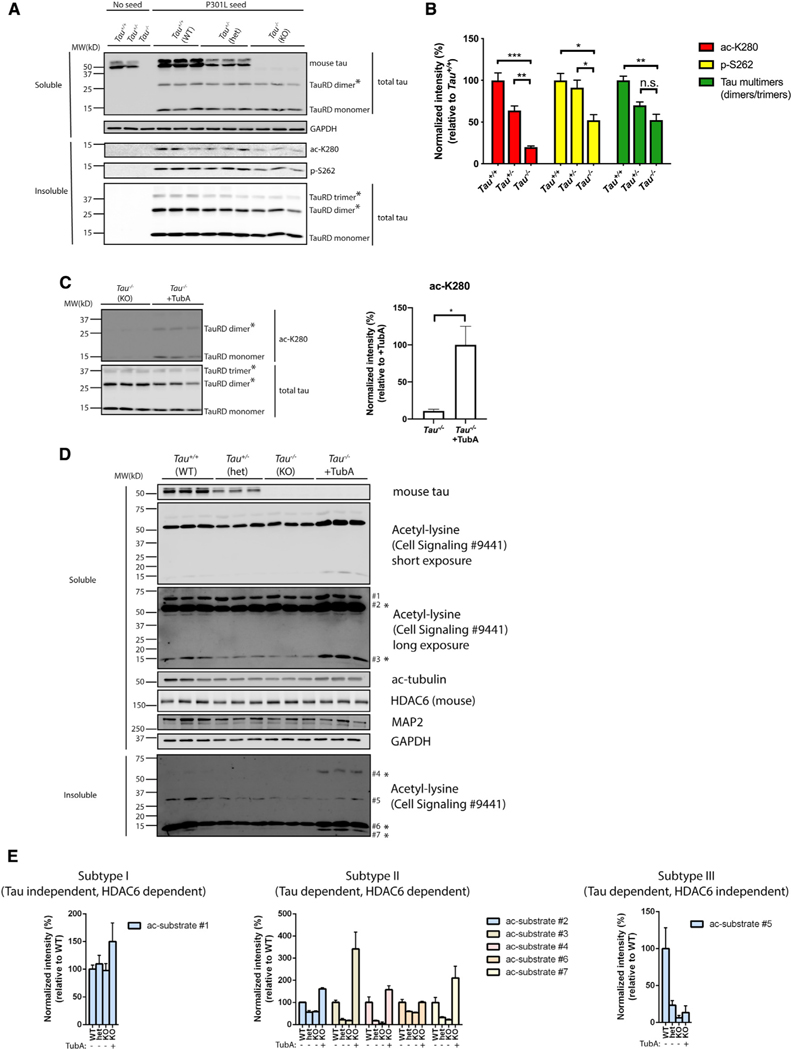
Figure 6. Tau reduction activates HDAC6.
(A) Primary Tau+/+, Tau+/−, and Tau−/−neurons were exposed to P301L tau seeds, fractionated into soluble and insoluble fractions, and analyzed by immunoblotting with site-specific tau antibodies (ac-K280 and p-S262), as well as a total tau antibody. TauRD dimers and trimers are highlighted with asterisks (*). GAPDH served as loading control.
(B) Quantification of site-specific modifications of P301L tau seeds in Tau+/+, Tau+/−, or Tau−/−neurons. Error bars indicate SEM; n = 3 biologically independent experiments. p value was determined by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s test for multiple comparisons among groups. n.s. p > 0.05, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
(C) Primary Tau−/−neurons were exposed to P301L tau seeds in the absence or presence of TubA (1 μM) and analyzed by immunoblotting with ac-K280 as well as a total tau antibody. The asterisks (*) highlight dimers and trimers. Acetylated tau seeds normalized to total tau levels were quantified on the right. Error bars indicate SEM; n = 3 biologically independent experiments. p value was determined by unpaired t test. *p < 0.05.
(D) Primary Tau+/+, Tau+/−, and Tau−/−neurons were left untreated or exposed to TubA (1 μM) overnight, fractionated into soluble and insoluble fractions, and analyzed by immunoblotting with a pan-acetyl-lysine antibody to reveal acetyl-lysine profile changes. Seven distinct acetylated substrates were detected by acetyl-lysine immunoreactivity and the protein bands were numbered accordingly. GAPDH served as loading control.
(E) The levels of acetylated substrates were quantified and classified as subtypes I–III based on correlations with tau genotype and responsiveness to the HDAC6 inhibitor TubA.