Figure 5.
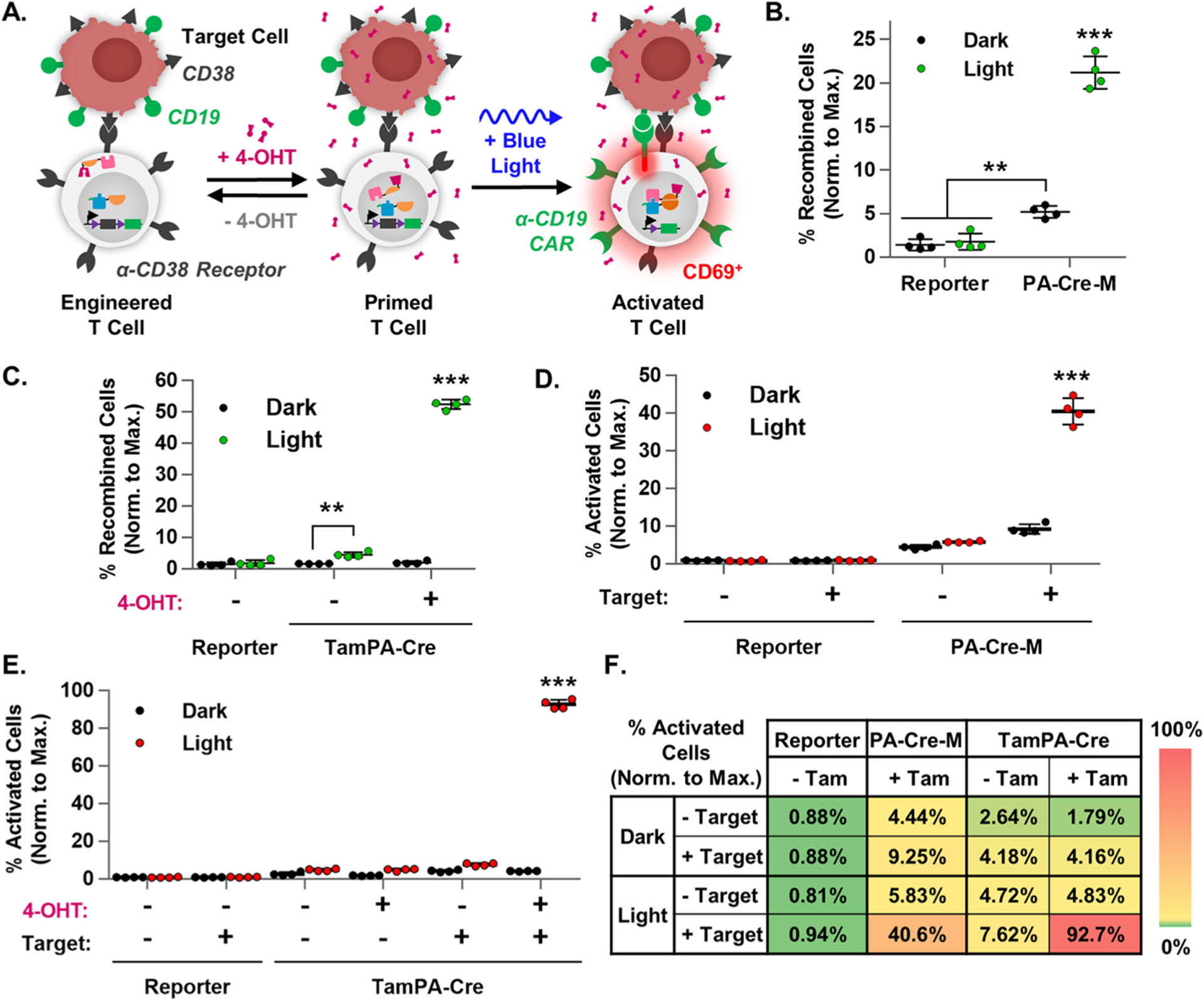
TamPA-Cre drives CAR-mediated T cell activation. (A) Schematic of the tamoxifen- and blue light-induced TamPA-Cre system in a CAR Reporter T cells driving recombination and CAR-mediated T cell activation upon binding to a TAA+ Target cells. The percentage of recombined cells (normalized to maximal recombination) in (B) PA-Cre-M+ and (C) TamPA-Cre+ CAR Reporter Jurkat T cells that did (+ 4-OHT) or did not (− 4-OHT) receive tamoxifen (500 nM) stimulation, and did (Light) or did not (Dark) receive blue light stimulation (473 ± 29 nm) as outlined in Protocol E (n = 4). The percentage of activated cells (normalized to maximal recombination) of samples from (B) and (C) that were (+ Target) or were not (− Target) coincubated with CD19+ Target cells (1:1), as reported in (D) and (E) respectively. (n = 4). (F) A heat map summary of T cell activation in Reporter, PA-Cre-M, and TamPA-Cre groups, with higher and lower efficiencies shown in red and green, respectively. Reporter = CAR Reporter Jurkat T cell line. Coincubation started and flow cytometry measurements taken 48 and 72 h after the start of blue light stimulation, respectively. Percentage of recombined Jurkat T cells (normalized to maximal recombination) = 100%*(% of CAR-EGFP+ cells)/(initial% of CAR Reporter+ cells, measured via myc). Percentage of activated Jurkat T cells (normalized to maximal recombination) = 100%*(% of CD69+ cells)/(initial % of CAR Reporter+ cells, measured via myc).
