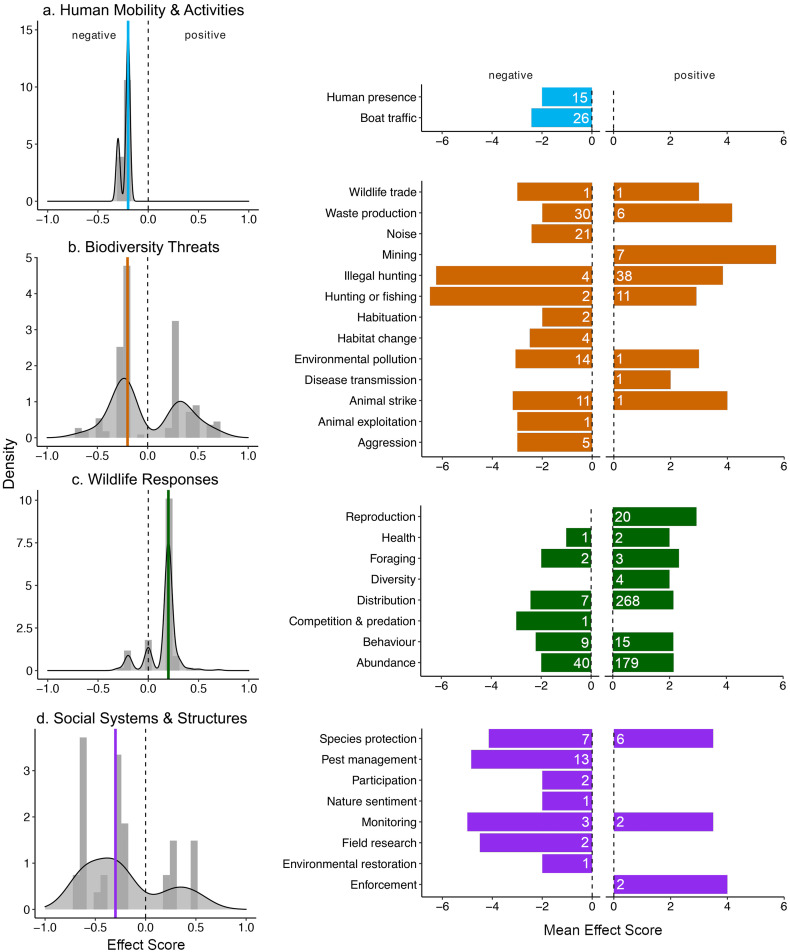
Fig. 4.
Qualitative negative and positive effects observed which were relative to the response observed (Appendix 4, Table A4). Negative effects indicate a dampening in the responses which were grouped into categories representing “Human Mobility & Activities”, Biodiversity Threats”, “Wildlife Responses” and “Social Systems & Structures”, while positive effects indicate an increase. The effect score is based on the criteria outlined in Appendix 1, Table A2, and considered the duration, spatial extent and total impact of the effect on the response. A negative or positive effect direction is relative to each category is based on the observed effect, rather than an interpreted impact. For instance, a negative effect on noise is a decrease in noise (which may have had positive wildlife impacts). a) Distribution of effects showing the direction and magnitude. The dotted line is the intercept, and the colored line indicates the median effect score. b) The mean effect score for categories falling within effects on human activities (blue), biodiversity threats (orange), biodiversity (green) and social systems (purple). Bars are the mean across reports pooled for positive and negative effects on the y-axis category, and white numbers are the number of observations upon which the mean is based. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)
Qualitative negative and positive effects observed which were relative to the response observed (Appendix 4, Table A4). Negative effects indicate a dampening in the responses which were grouped into categories representing “Human Mobility & Activities”, Biodiversity Threats”, “Wildlife Responses” and “Social Systems & Structures”, while positive effects indicate an increase. The effect score is based on the criteria outlined in Appendix 1, Table A2, and considered the duration, spatial extent and total impact of the effect on the response. A negative or positive effect direction is relative to each category is based on the observed effect, rather than an interpreted impact. For instance, a negative effect on noise is a decrease in noise (which may have had positive wildlife impacts). a) Distribution of effects showing the direction and magnitude. The dotted line is the intercept, and the colored line indicates the median effect score. b) The mean effect score for categories falling within effects on human activities (blue), biodiversity threats (orange), biodiversity (green) and social systems (purple). Bars are the mean across reports pooled for positive and negative effects on the y-axis category, and white numbers are the number of observations upon which the mean is based. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)