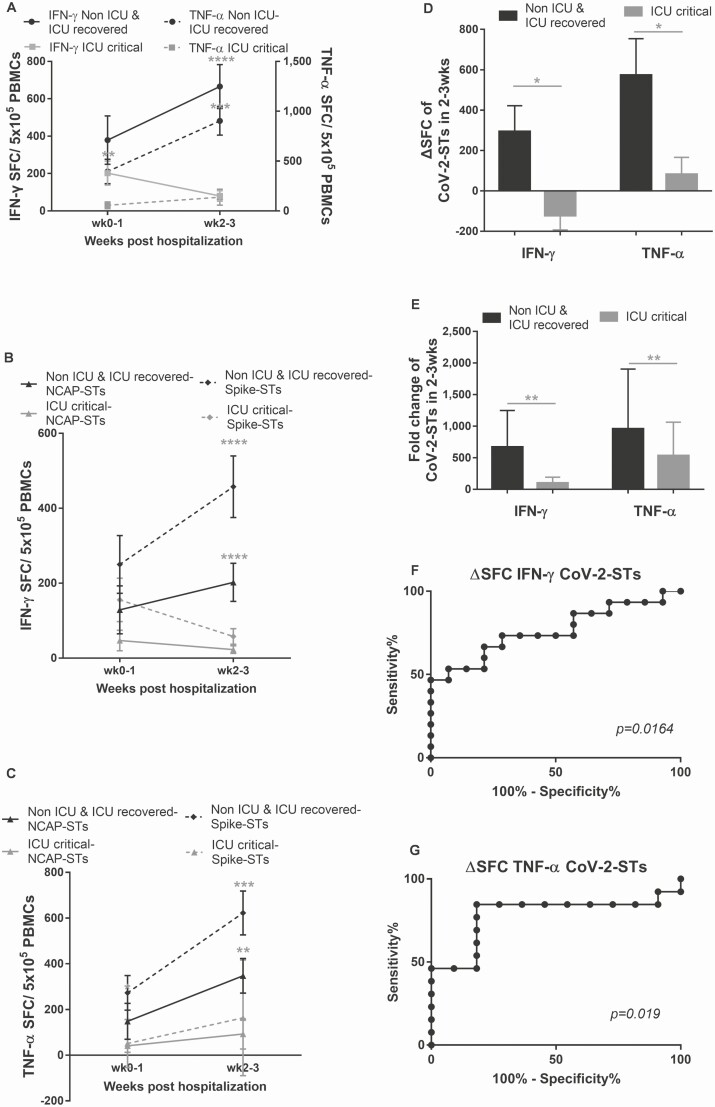
Figure 2.
Kinetics of endogenous circulating severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)–specific T cells (CoV-2-STs) in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). A, The expansion of interferon gamma (IFN-γ)– and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α)–secreting endogenous CoV-2-STs in response to SARS-CoV-2 antigens postadmission to the clinic or intensive care unit (ICU) is associated with a favorable disease outcome (IFN-γ Non-ICU and ICU recovered, n = 14; IFN-γ ICU critical, n = 14; TNF-α Non-ICU/ICU recovered, n = 14; TNF-α ICU critical, n = 14). Differences between data sets were analyzed using Mann-Whitney test. **P = .0093; ***P = .0002; ****P < .0001. B and C, The expansion of IFN-γ (B)– and TNF-α (C)–secreting endogenous CoV-2-STs in response to NCAP or spike antigens postadmission to the clinic or ICU is associated with a favorable disease outcome (IFN-γ Non-ICU and ICU recovered, n = 14; IFN-γ ICU critical, n = 14; TNF-α Non-ICU/ICU recovered, n = 14; TNF-α ICU critical, n = 14). Differences between data sets were analyzed using Mann-Whitney test. **P = .0032; ***P = .0006; ****P < .0001. D and E, Δ spot-forming cells instead of units (ΔSFC; D) or fold change (E) of IFN-γ– and TNF-α–secreting circulating CoV-2-STs postadmission to the clinic or ICU (Non-ICU and ICU recovered, n = 15; ICU critical, n = 14). Differences between data sets were analyzed using Mann-Whitney test. *P ≤ .0184; **P ≤ .0061. F and G, Receiver operating characteristic curves of the ΔSFC of circulating IFN-γ (n = 29; F)– and TNF-α (n = 24; G)–secreting CoV-2-STs showing the predictive power of COVID-19 favorable outcome (high probability to self-control the infection). Abbreviations: CoV-2-ST, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2–specific T cell; ICU, intensive care unit; IFN-γ, interferon gamma; NCAP, nucleocapsid protein; PBMC, peripheral blood mononuclear cell; SFC, spot-forming cell; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor alpha.