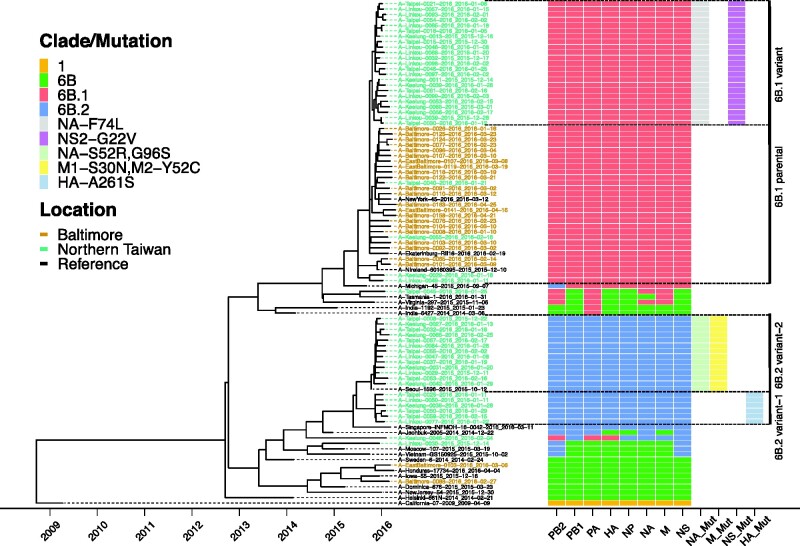
Figure 2.
Four distinct genetic subgroups of H1N1pdm were identified in Baltimore and Northern Taiwan in the 2015–16 season. ML trees of concatenated gene segments of 73 H1N1pdm viruses of the surveillance were generated using RAxML under GTRGAMMA model with 1,000 bootstrap replicates. Their time scales based on sample collection dates, noted in each sample, were calibrated using coalescent model in TreeTime after building ML trees. Reference sequences are H1N1pdm vaccine strains, A/California/07/2009 and A/Michigan/45/2015 and three 6B.1, two 6B.2 and thirteen 6B viruses. Tips were colored by location of sample collection. Samples from Baltimore were colored in brown; samples from northern Taiwan were colored in green. A schematic representation of clade/mutation of each gene segment based on their individual gene tree branches to separate annotated clades (1, 6B, 6B.1 or 6B.2) and amino acid mutations (see Supplementary Fig. S1) was annotated and visualized using the ggtree R package. Mutations (Mut) in NA, M, NS and HA segments were identified to be able to divide majority of viruses into four distinct genetic subgroups, 6B.1 parental, 6B.1 variant, 6B.2 variant-1 and 6B.2 variant-2.