Fig. 2 |. T cell early and late signaling aberrations in T cells from patients with SLE.
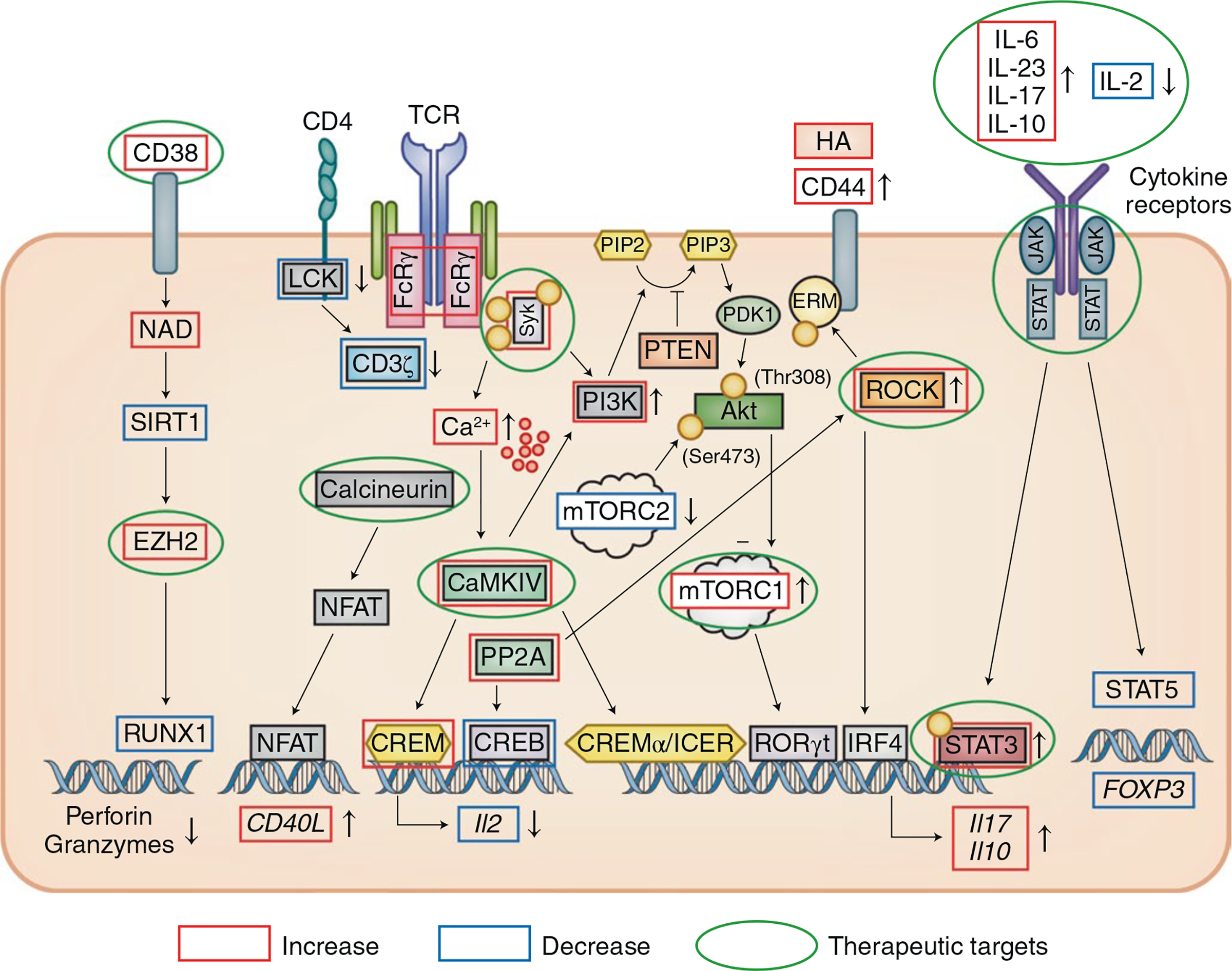
Engagement of the CD3 complex either by autoantigen or circulating CD3/TCR antibodies results in an increased intracytoplasmic calcium response. The CD3 complex is rewired, with the CD3ζ chain replaced with the FcRγ chain, which recruits the kinase Syk. The calcium-requiring kinase CaMKIV enhances the binding of CREMα/ICER to the Il2 and Il17 or Il10 promoters to suppress and enhance their expression, respectively. Calcineurin also dephosphorylates the transcription factor NFAT, which binds to the promoter of CD40L and increases its expression. Phosphatase PP2A is increased in T cells with diverse effects: in Treg cells, it dephosphorylates mTORC1 and promotes Treg cell function and, in effector T cells, it enhances the binding of IRF4 to the Il17 promoter and it dephosphorylates p-CREB. PP2A also promotes ROCK activity, which phosphorylates ERM, which in turn enhances the ability of CD44 to bind its ligand hyaluronic acid (HA, expressed in the kidney and other tissues). IL-2 signaling is defective with decreased amounts of p-STAT5, whereas IL-6 signaling is increased with increased binding of p-STAT3 to the Il17 promoter. An increased proportion of CD8+ T cells express the ectonucleotidase CD38, which suppresses the level of NAD and the activity of the deacetylase SIRT1, which in turn enhances the activity of the histone methyltransferase EZH2. As indicated by the green circles, a number of the molecules have been considered as therapeutic targets: Syk, ROCK, calcineurin, EZH2, IL-17, IL-23, JAK and mTOR as well as IL-2, which can be replenished with low doses.
