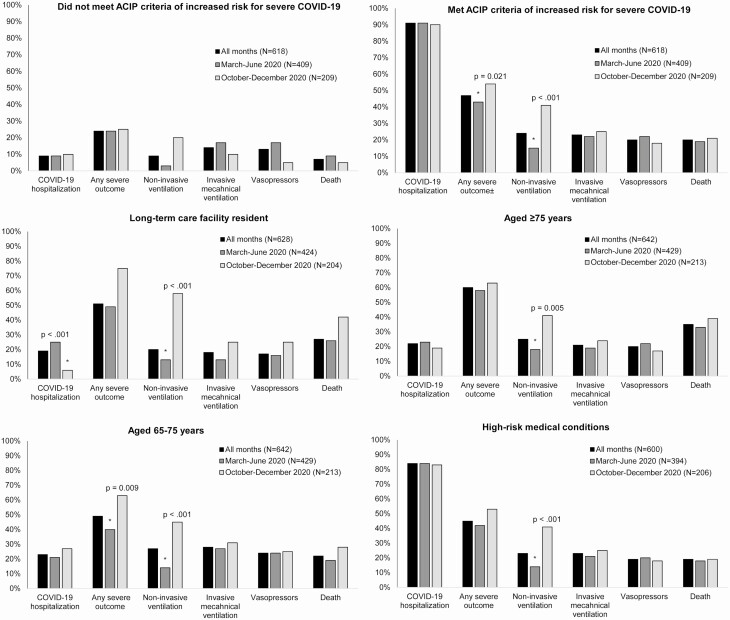
Figure 1.
Outcomes among hospitalized adults testing positive for SARS-COV-2 by ACIP priority group for vaccine allocation and by time period—14 Academic Medical Centers, United States, March–June and October–December 2020.
*Denotes a significant P-value. χ 2 or Fisher exact test were used for statistical testing of categorical variables. ACIP criteria of increased risk for severe COVID-19 include: long-term care facility residents, persons aged ≥65 years, and persons aged 16–64 years with high-risk medical conditions associated with increased risk for severe COVID-19 defined by CDC (cancer; chronic kidney disease; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; heart conditions [eg, heart failure, coronary artery disease, or cardiomyopathies]; immunocompromised state from solid organ transplant; obesity; sickle cell disease; smoking; diabetes mellitus; and pregnancy) [1]. Some severity subgroups were missing data (from 4% to 6%): any severe outcome (March–June: 26, October–December: 3), noninvasive ventilation (March–June: 34, October–December: 4), invasive mechanical ventilation (March–June: 29, October–December: 3), and vasopressors (March–June: 32, October–December: 2). Denominators used to calculate proportions of respondents with select outcomes in the specified group excluded patients who had missing data. Any severe outcome was defined as: noninvasive ventilation, invasive mechanical ventilation, vasopressor support, dialysis/renal replacement therapy, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, stroke, venous thromboembolic event, or death. Abbreviations: ACIP, Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices; CDC, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; COVID-19, coronavirus disease 2019; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.