Fig. 6. Broad distribution of LGE-derived interneurons in the songbird brain.
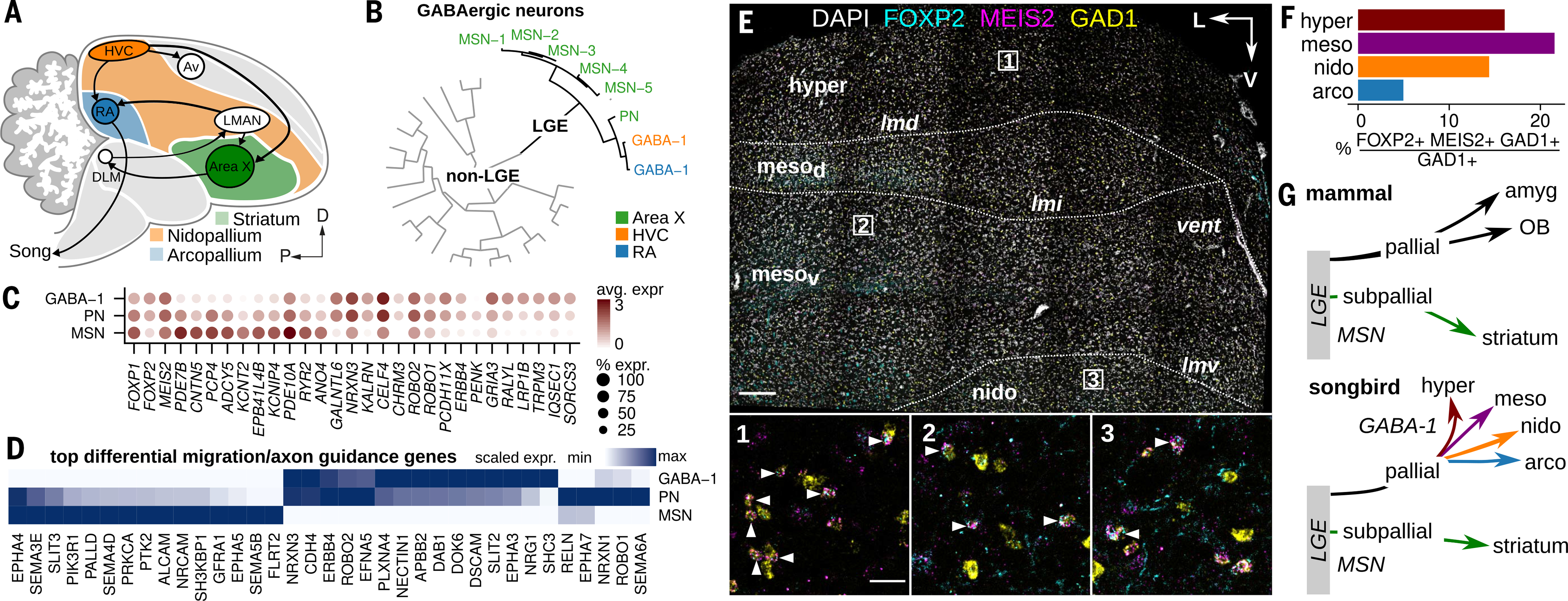
(A) Schematic illustrating the location of Area X within the avian striatum (green) in relation to the nidopallium (orange) and arcopallium (blue). (B) Hierarchical clustering of HVC, RA, and Area X GABAergic neuron expression profiles, divided by LGE-class and non-LGE-class neurons. PN, pallidal-like neuron. (C) Expression of top differentially expressed genes in LGE-derived GABAergic classes and three genes associated with striatal GABAergic neurons (FOXP1, FOXP2, and MEIS2). Shade of dot represents mean expression within cluster, and size of dot represents percentage of cells within the cluster expressing that gene. (D) Scaled expression of top differentially expressed axon guidance and neuron migration related genes across avian LGE-class neurons. (E) Three-color in situ hybridization of LGE-marker genes FOXP2 and MEIS2 and GABAergic marker gene GAD1. Shown is a coronal section from the anterior Bengalese finch brain. Major anatomical divisions: hyper, hyperpallium; mesod, dorsal mesopallium; mesov, ventral mesopallium; nido, nidopallium; Lamina: lmd, dorsal mesopallial lamina; lmi, intermediate mesopallial lamina; lmv, ventral mesopallial lamina. Nomenclature is as defined in (13). Scale bar, 200 μm. (Insets) Magnifications of three regions indicated in the main panel. Arrowheads indicate triple-positive cells. Scale bar, 50 μm. (F) Quantification of FOXP2/MEIS2/GAD1 in situ hybridization data, shown as percentage GAD1-positive cells in four pallial domains that coexpress FOXP2 and MEIS2. (G) Comparison of LGE-class GABAergic migration in mammals and songbirds. In mammals, the LGE contributes neurons in the pallial amygdala (intercalated cells), the olfactory bulb (granule and periglomerular interneurons), and subpallial structures such as the striatum (MSNs). Amyg, pallial amygdala.
