Figure 1. Biogenesis and clearance of H2S and reactive sulfur species.
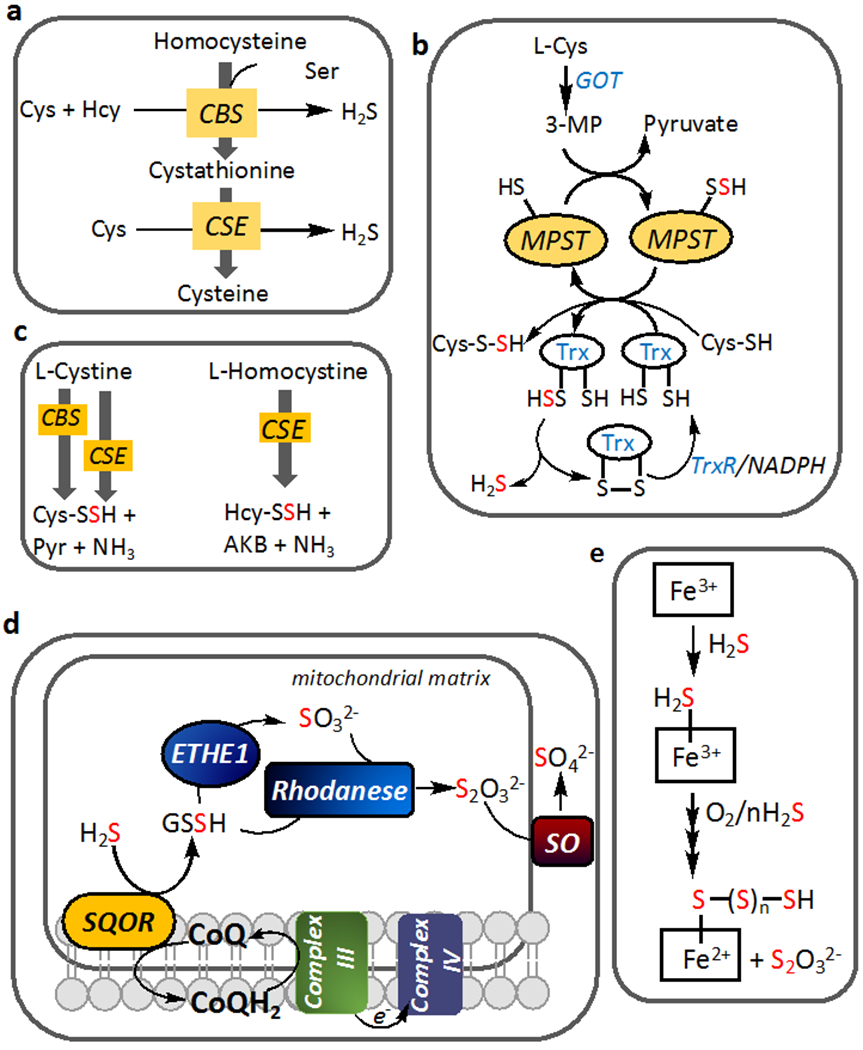
(a) Reactions showing the major routes for H2S synthesis by CBS and CSE at cellular concentrations of substrates and their canonical reactions in the transsulfuration pathway. (b) H2S generation by MPST from 3-mercaptopyruvate (3-MP), which is derived from cysteine via the action of glutamate-oxaloacetate transaminase (GOT), which is also referred to as cysteine aminotransferase. A persulfide intermediate is formed on MPST and transferred to a low molecular weight (LMW) acceptor like cysteine or to thioredoxin (Trx). TrxR represents thioredoxin reductase. (c) LMW persulfides can be synthesized by CBS and CSE, with the latter being the major source under cellular conditions. Pyr and AKB denote pyruvate and α-ketobutyrate. (d) The mitochondrial sulfide oxidation pathway enzymes lead to oxidation of H2S to thiosulfate and sulfate. Electrons from the first step in the pathway, which is catalyzed by SQOR (sulfide quinone oxidoreductase), enter the ETC at the level of complex III. ETHE1 is a persulfide dioxygenase and SO denotes sulfite oxidase (e) Sulfide can be oxidized at ferric heme centers in globins leading to formation of thiosulfate and iron bound polysulfides.
