Figure 3. Metabolic pathways that are potentially affected by H2S.
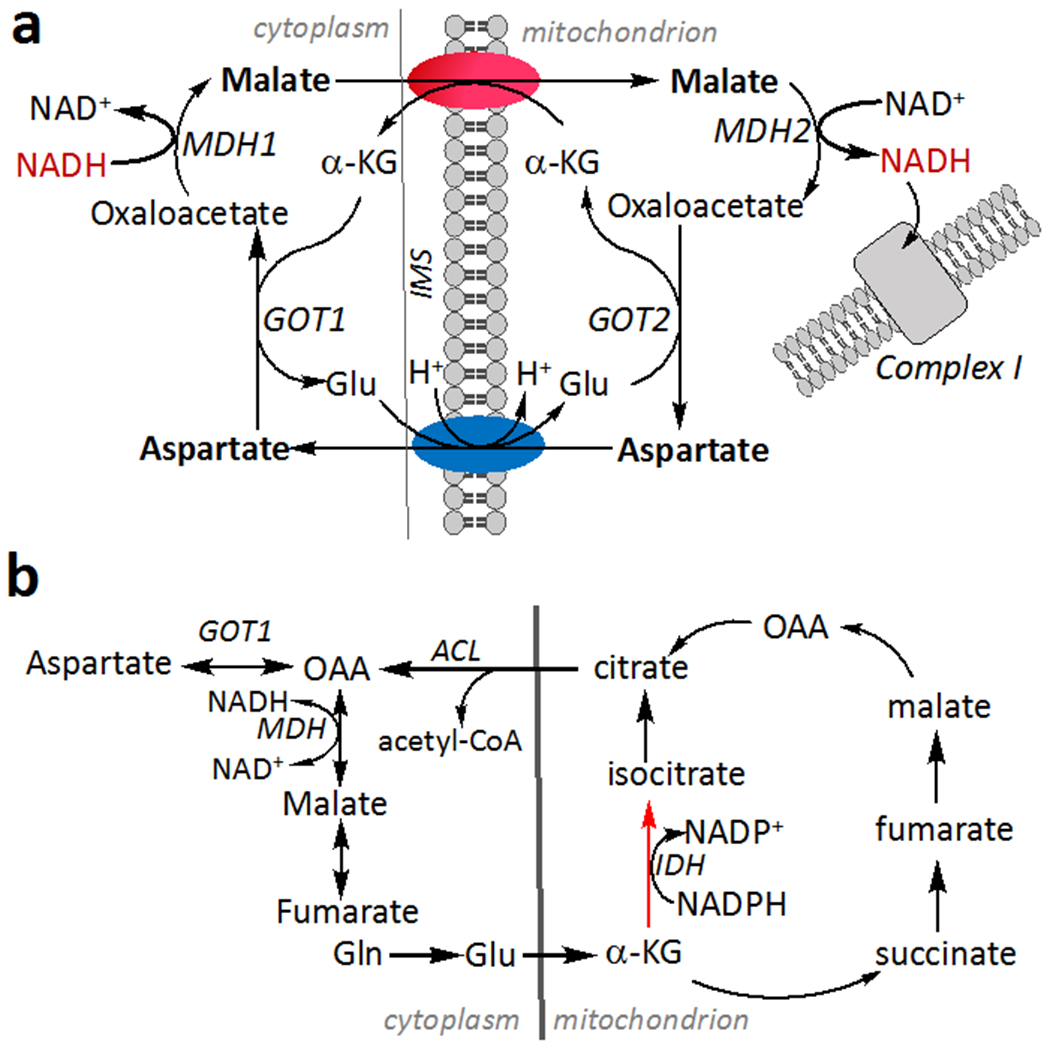
(a) The malate aspartate shuttle transfers NADH equivalents as malate, which crosses the mitochondrial inner membrane via a reversible α-ketoglutarate/malate carrier. Aspartate generated in the mitochondrion is exchanged for glutamate by an electrogenic carrier and converted to malate via the activity of cytosolic glutamate oxoglutarate transaminase (GOT1). (b) H2S stimulates reductive carboxylation (red arrow), which is catalyzed by isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH). Cleavage of citrate by acetyl-CoA lyase (ACL) provides an alternative source of cytosolic oxaloacetate (OAA), which is converted by GOT1 to aspartate. IMS is inter mitochondrial membrane space.
