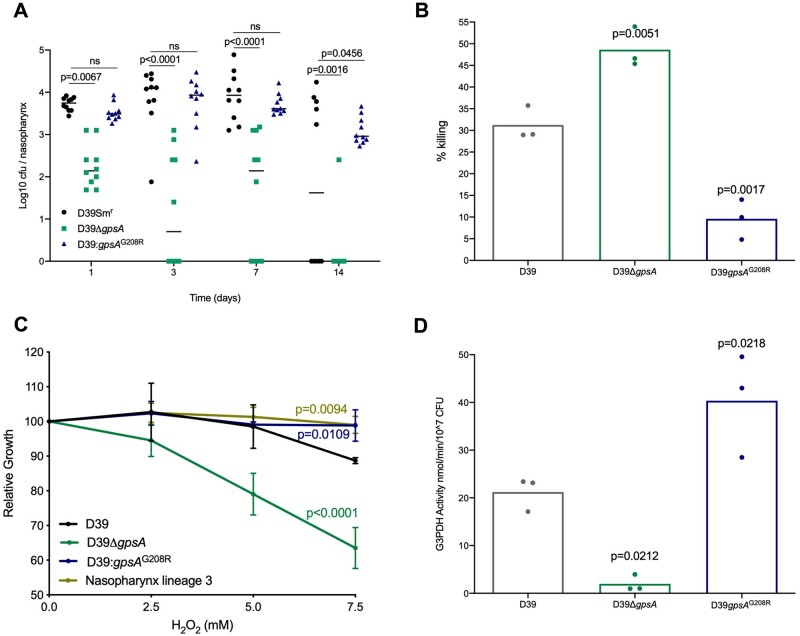
Fig. 7.
Glycerol-6-phosphate dehydrogenase is required for effective colonization of nasopharynx. (A) Mice were infected with a nasopharyngeal carriage-inducing dose of a streptomycin-resistant version of the ancestor D39 in which either a clean deletion of gpsA (D39ΔgpsA) or the SNP causing the G208R substitution (D39: gpsAG208R) had been generated. Control animals were infected with the streptomycin-resistant D39 ancestor expressing wild type gpsA (D39Smr). Bacterial numbers were determined by serial dilution of nasopharynx homogenates onto selective agar at days 1, 3, 7, or 14 postinfection. N = 10 per group. P-values are from two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparison test. (B) CFU counts following 30 min incubation in a 12 mM hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) solution. Data are presented as percentage killing vs the no H2O2 control for each strain. P-values are from a one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test vs D39. (C) Percentage reduction in growth (measured as area under the logistic curve [AUC]) for D39, D39gpsA, D39gpsAG208R, and nasopharynx lineage 3 in the presence of increasing concentrations of H2O2. P-values are from a two-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test versus D39. Each point is the mean of three biological replicates, each containing three technical replicates. Error bars are standard deviation. (D) Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (G3PDH) enzyme activity measured using a colorimetric assay. Activity was determined relative to a NADH standard curve and is presented as nmol NADH per minute per 107 CFU. P-values are from a one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test versus the D39 ancestor. (B, D) Each data point represents a single biological replicate, each of which is the mean of three (B) or two (D) technical replicates.