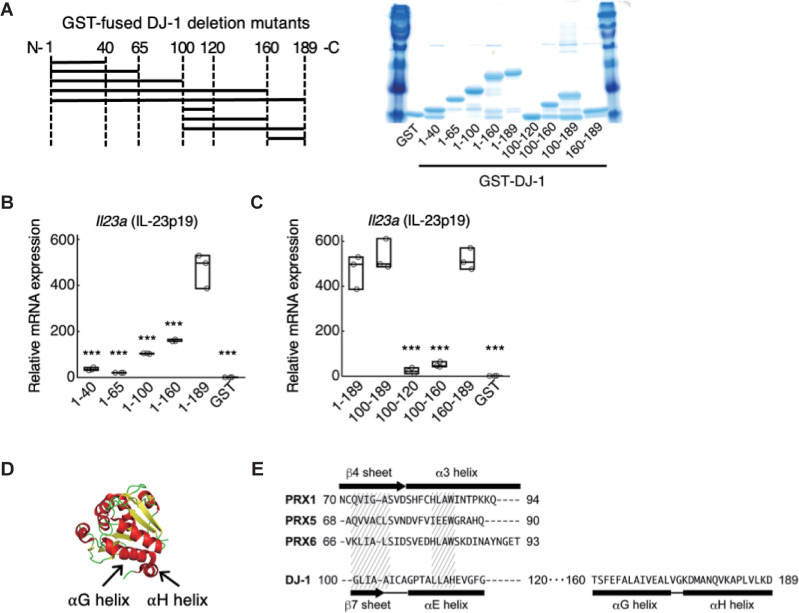
Fig 3. The αG and αH helix region of DJ-1 is essential for DAMP activity.
(A) Diagram of generated deletion mutant peptides of DJ-1 fused with GST (left panel). The number of amino acid residues contained in each GST-fused DJ-1 peptide is shown on the x-axis. The amount of generated deletion mutant peptides was examined by SDS-PAGE with CBB staining (right panel). (B) IL-23p19-inducing activities of carboxyl-terminal deletion mutants of DJ-1. (C) IL-23p19-inducing activities of GST-fused peptides containing the carboxyl-terminal region of DJ-1. (D) αG helix (DJ-1160–173: peptides between residues 160 and 173 of DJ-1) and αH helix (DJ-1175–189) are indicated in the crystal structure of DJ-1 protein (PDB ID: 1P5F). (E) Comparison of peptide sequences among PRX170–94, PRX568–90, and PRX666–93 containing the β4 sheet and α3 helix of PRXs known to be important for DAMP activity, DJ-1100–120 containing the β7 sheet and αE helix, and DJ-1160–189 containing the αG and αH helix. Similarities among the amino acid residues of PRXs and DJ-1 are indicated by hatched areas. ***p < 0.001 vs. BMMs treated with DJ-11–189 (B, C) (one-way ANOVA with Dunnett correction [B, C]). Experiments were performed in triplicate, and the results are representative of 2 independent experiments (B, C). The data underlying this figure can be found in S1 Data. ANOVA, analysis of variance; BMM, bone marrow–derived macrophage; CBB, Coomassie brilliant blue; DAMP, damage-associated molecular pattern; GST, glutathione-S-transferase; PRX, peroxiredoxin.