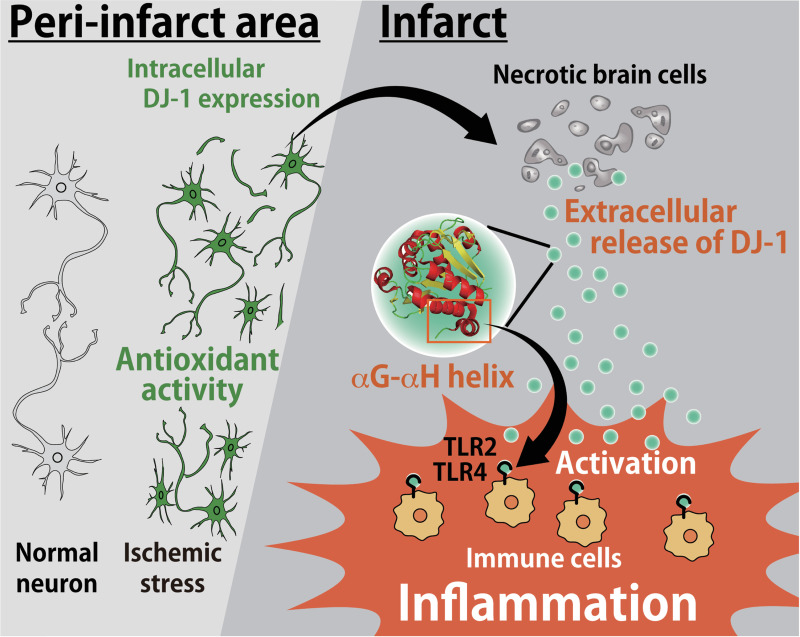
Fig 7. Schematic model of the roles of DJ-1 in the ischemic brain injury.
In the peri-infarct area, the expression level of DJ-1 within the neurons increases due to ischemic stress. Intracellular DJ-1 plays a neuroprotective role by catalyzing ROS whereas if ischemic stress results in neuronal cell death, accumulated DJ-1 within ischemic neurons is passively released into the extracellular space. The αG–αH helix of extracellular DJ-1 directly activates TLR2 and TLR4 in infiltrating immune cells to trigger sterile inflammation. Therefore, DJ-1 has 2 opposing functions: extracellularly (inflammatory molecule as a DAMP) and intracellularly (antioxidant activity) in the pathology of ischemic stroke. DAMP, damage-associated molecular pattern; ROS, reactive oxygen species.