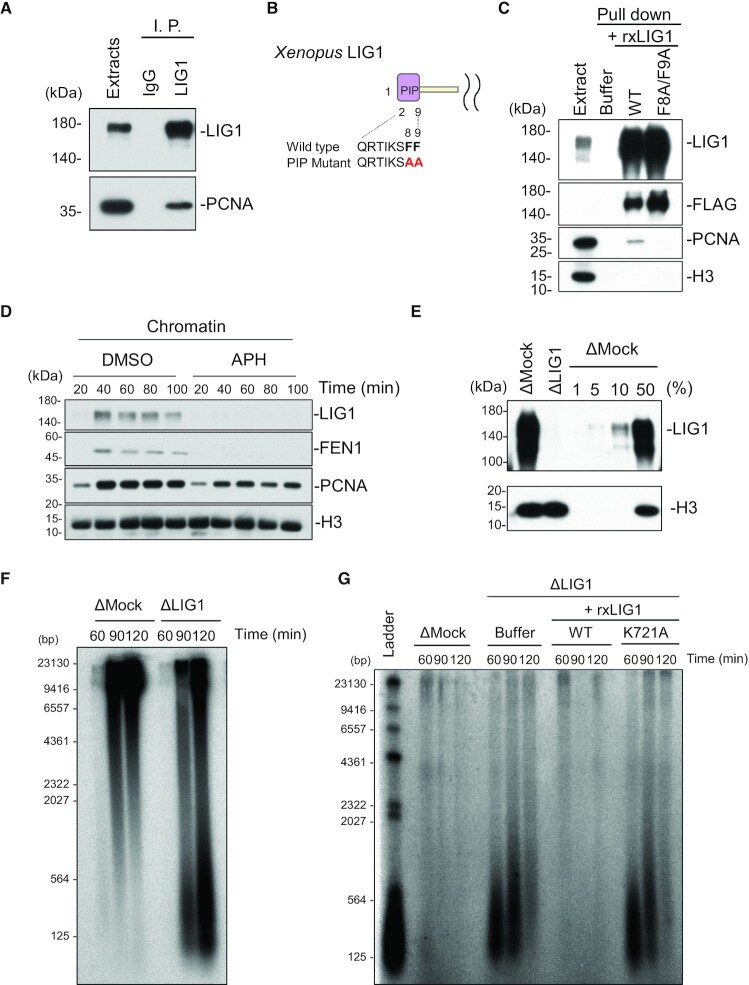
Figure 1.
Depletion of LIG1 inhibits Okazaki fragment ligation in Xenopus egg extracts. (A) Control or xLIG1 antibodies were used for immunoprecipitation (I. P.) and immunoprecipitated proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting using the indicated antibodies (n = 2). (B) Sequences of the wild-type and the F8A/F9A mutant PIP-box in xLIG1 are shown. (C) Recombinant wild-type xLIG1–3 × Flag or xLIG1-F8A/F9A-3 × Flag was added to the egg extracts. Immunoprecipitation using anti-Flag antibodies was performed and resultant immunoprecipitates were analyzed by immunoblotting using the indicated antibodies (n = 2). (D) Interphase egg extracts were added with sperm chromatin and incubated in the presence of 30 μM aphidicolin or in its absence (DMSO). Chromatin fractions were isolated and analyzed by immunoblotting using the indicated antibodies (n = 2). (E) Immunodepletion efficiency of xLIG1 from Xenopus egg extract (n = 3). (F) Replication products in mock- or xLIG1-depleted extracts were separated by alkaline agarose gel electrophoresis followed by autoradiography (n = 2). (G) xLIG1-depleted extracts were supplemented with wild-type xLIG1–3 × Flag or xLIG1-K721A-3 × Flag and chromatin was isolated. Purified genomic DNA from chromatin was labeled using exonuclease-deficient Klenow fragment and α-32P dCTP, and separated in a denaturing agarose gel (n = 2).