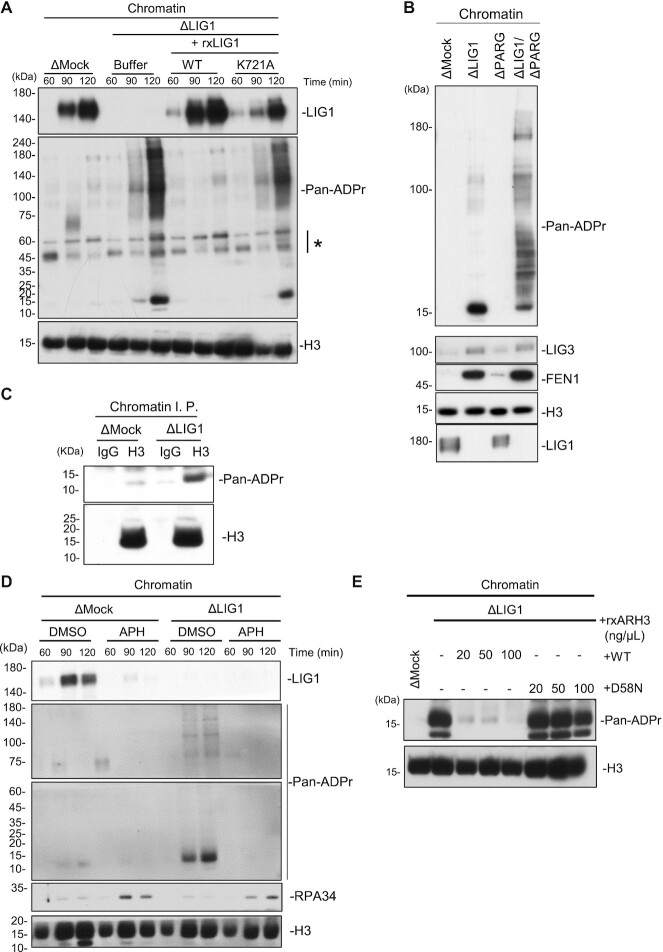
Figure 3.
LIG1 deficiency causes histone H3 ADP-ribosylation. (A) Mock- and xLIG1-depleted extracts were used for replication of sperm chromatin. xLIG1-depleted extracts were supplemented with wild-type xLIG1 or xLIG1-K721A. Chromatin-bound proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting using the indicated antibodies and pan ADP-ribose (Pan-ADPr) detecting reagent (n = 3). The asterisk indicates a non-specific band. (B) Mock-, xLIG1-, xPARG- and xLIG1/xPARG-depleted extracts were used for replication of sperm nuclei. Chromatin-bound proteins were analyzed as in Figure 3A (n = 2). (C) Chromatin fractions from the indicated immunodepleted extracts were solubilized with MNase followed by immunoprecipitation with anti-histone H3 antibodies after treatment with 1% SDS. The resultant immunoprecipitates were analyzed as in Figure 3A (n = 2). (D) Mock- and xLIG1-depleted extracts were used for replication of sperm nuclei in the presence of 30 μM APH where indicated. Chromatin-bound proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting using the indicated antibodies and pan ADP-ribose detecting reagent (n = 2). (E) Mock- and xLIG1-depleted extracts were used for replication of sperm chromatin. xLIG1-depleted extracts were supplemented with either buffer or recombinant wild-type His10-xARH3 or His10-xARH3-D58N, (0.2–1 μM). Chromatin-bound proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting using the indicated antibodies and pan ADP-ribose detecting reagent (n = 2).