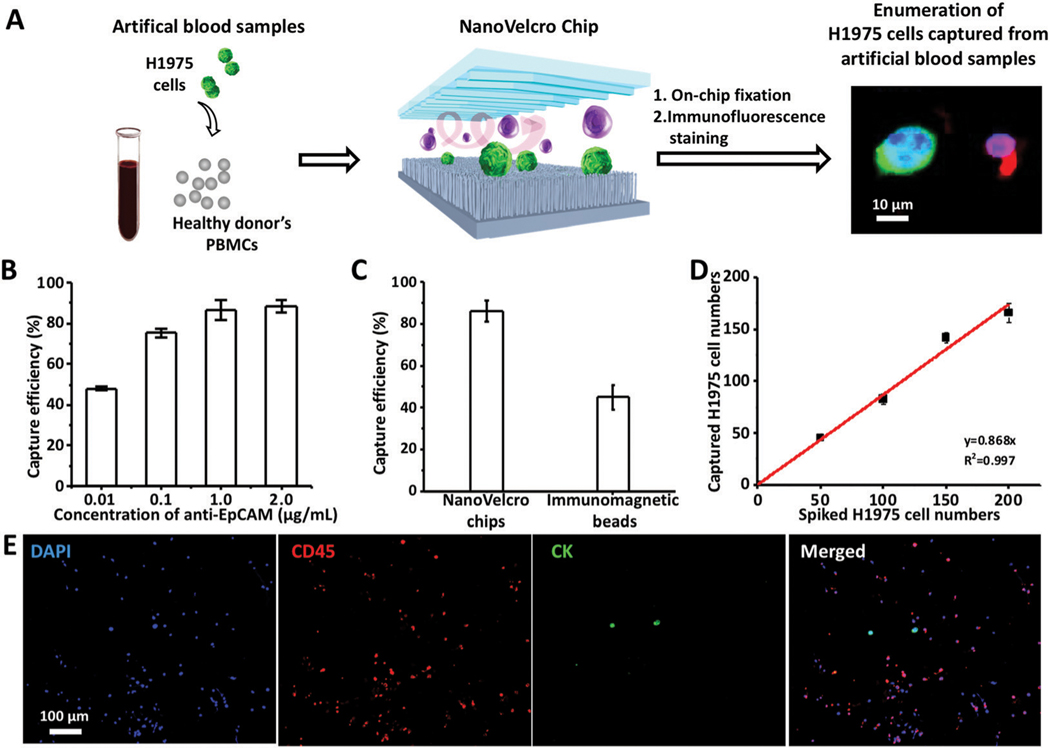
Fig. 2.
Optimization and validation of NanoVelcro Chips for the capture of NSCLC CTCs using artificial blood samples. (A) Workflow summarizes the CTC enrichment of NanoVelcro Chips using artificial blood samples, prepared by spiking H1975 cells in the PBMCs from healthy donors. Immunofluorescence staining was employed to enumerate captured CTCs for calculating the capture efficiency. (B) CTC-capture efficiency of NanoVelcro Chips was studied at anti-EpCAM concentrations of 0.01, 0.1, 1.0 and 2.0 μg mL−1. (C) Comparison of the capture efficiencies of CTCs on NanoVelcro Chips and immunomagnetic beads. (D) Dynamic ranges observed for NSCLC CTC capture efficiency using artificial blood samples spiked with different amounts of H1975 cells under the optimal capture conditions. (E) Representative fluorescence micrographs of WBCs (DAPI+/CK−/CD45+) and CTCs (DAPI+/CK+/CD45−) captured from artificial blood samples using NanoVelcro Chips.